Due to the increasing population and changes in the natural environment caused by climate change, the demand for water is expected to increase, and social concern for the preservation of water resources is increasing.
MITSUBISHI MOTORS Group requires a large amount of industrial water, city water, and groundwater, etc., in automobile production process and discharges of water into sewage lines and rivers, etc. We have identified “Conservation of Water Resources” as a material issue. As measures to preserve water resources in each country and region, we strive to reduce the amount of water withdrawal and to monitor the quality of discharged water.
At business sites, we comply with various legal requirements, such as on the quality of discharged water. In addition, we work to reduce water withdrawal amounts and introduce water recycling technologies based on the status of water resource management in individual countries and regions. PT. Mitsubishi Motors Krama Yudha Indonesia (MMKI) and Mitsubishi Motors (Thailand) Co., Ltd. (MMTh) have installed waste water recycling plants to allow the reuse of waste water.
Reduction of Water Withdrawal Volume
We are striving to reduce water withdrawal volumes by reusing washing water used in production processes for pre-washing and by circulating cooling water and temperature control water.
Please refer to the following section for topics related to the reduction of water withdrawal volume.
-

Rainwater storage tank
(Okazaki Plant) -

Groundwater membrane filtration equipment
(Okazaki Plant)
TOPICS
Recycling Condensate from Air Conditioners Used at Painting Facilities (MMTh)
Mitsubishi Motors (Thailand) Co., Ltd. (MMTh) has begun recycling condensate from air conditioners used at its vehicle painting facilities. The Thai environment is hot and humid throughout the year, so condensate is steadily obtained from the dehumidification process of air conditioners. This condensate is collected in a water storage tank and reused as part of the water supply to the cooling tower for the chillers, thereby reducing the water supply to the cooling tower by about 30%, or 100 m3/day. Furthermore, utilizing low-temperature (approx. 23°C) condensate helps to improve cooling towers’ cooling efficiency.
-
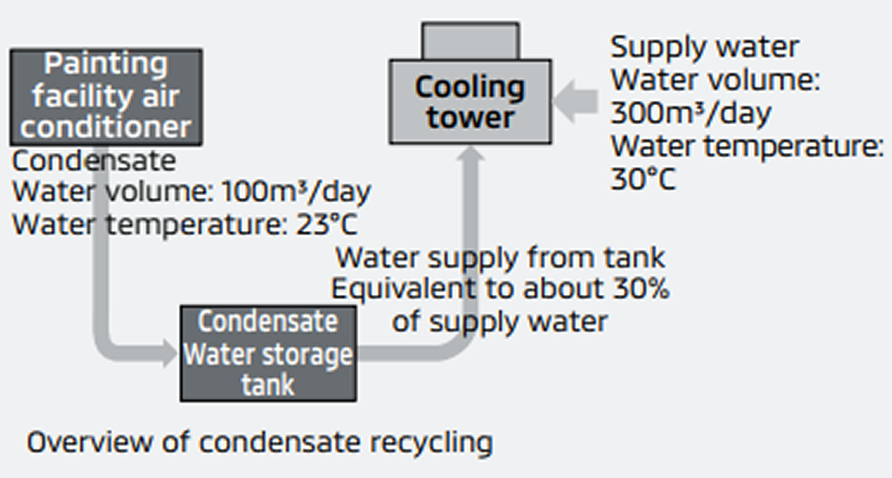
Overview of condensate recycling
-

Installed condensate water storage tank
Reuse of Discharged Water
The MITSUBISHI MOTORS Group has introduced wastewater recycling technologies, taking into consideration the situation regarding water resource management at each facility location.
Currently, discharged water recycling plants are operational at PT Mitsubishi Motors Krama Yudha Indonesia (MMKI) and Mitsubishi Motors (Thailand) Co., Ltd. (MMTh).MMKI has been utilizing awastewater recycling plant since its establishment in 2017. In FY2024, its wastewater recycling rate reached 75%. MMTh put its wastewater recycling plant into operation in January 2022, and in FY2024, its wastewater recycling rate was 79%.

Wastewater recycling plant (MMTh)
Prevention of Water Pollution
To prevent water pollution in areas surrounding plants, we measure and manage the quality of discharged water based on legal requirements. We also conduct surveys and confirmations regarding the quality of groundwater and soil pollution. In this way, we confirm that no toxic substances are being discharged to the outside area. In order to quickly detect abnormalities in discharge water quality due to such factors as rainfall, we set up a surface oil detector(*) in front of outlets leading from the plant to public water and continuously monitor discharge water conditions. We carry out continuous monitoring so that water discharged from the plant does not affect the environment outside the site. In the event of an accident, we respond quickly to prevent pollution from spreading, report to the local authorities and disclose information to the community.
- Detects the presence of oil by capturing changes in reflectance as the reflectance of oil is greater than that of water
-

Observation well (Okazaki Plant)
-

Surface oil detector (Okazaki Plant)
TOPICS
Installation of a Manhole-Type Oil-Water Separator (Kyoto Plant)
At Kyoto Plant–Kyoto, we installed a manhole-type oil-water separator in front of the oil film detector as an enhanced measure to prevent the leakage of pollutants from road surfaces within the plant. Oil film detectors have traditionally been used to monitor oil leakage from stormwater outlets at factories. However, after referring a “Non-Specified Pollution Source Countermeasures” case study of measures used for busy roads, factories, and commercial facilities, we installed a new manhole-type oil-water separator in front of the oil film detector in the rainwater drainage path. This allows for the separation and discharge of suspended solids and oil from road surface drainage during wet weather.

Manhole-type oil-water separator installed in the storm drainage path