Basic Approach
The rise in populations and economic growth in emerging markets is leading to a rise in the consumption of minerals, fossil fuels and other resources.
The MITSUBISHI MOTORS Group is working to use fewer resources and use them more effectively in automobile manufacturing processes so that we can add more value to vehicles. We therefore see the effective use of resources as an important priority. The Environmental Plan Package positions resource recycling as an environmental issue for our Group to engage with directly, and we are contributing to a resourcerecycling-oriented society by minimizing input resources and maximizing resource efficiency.
Countries and industry groups are formulating various initiatives in order to promote automobile recycling and correct processing. In response, we set targets to improve the ease of recycling, reduce the use of lead, and introduce recycled parts for new vehicles when the “MITSUBISHI MOTORS Recycling Initiative” was established in 1998. We have continued to engage in this initiative.
Recycling-Based Design and Development
Under vehicle recycling legislation in Japan, Europe, China, and other countries, automobile manufacturers are obligated to consider recycling when developing products. We conduct design and development that actively incorporates not just recycling,but all aspects of the 3Rs including reduction and reuse. We are also expanding adoption of non-fossil-based plastic such as recycled materials and biomass plastics in vehicles.
Recycled used clothing materials are used for silencer parts such as dashboards, and biomass plastics are used for interior parts such as steering wheel garnishes.
At dealers, bumpers recovered or replaced during repairs are recycled for use in battery trays and other exterior parts. We plan to carry out further development to continue to expand our adoption of non-fossil-based plastic.
TOPICS
Using Thermoplastic Resin
The “XFORCE (HEV model)” which was launched in 2024, uses easily recyclable thermoplastic resin*1 for exterior and interior parts.
- Thermoplastic resin: A plastic that resists deforming at room temperatures, but softens and becomes easy to mold when heated, and hardens again when cooled
Main parts (indicated in green) that use thermoplastic resin
-
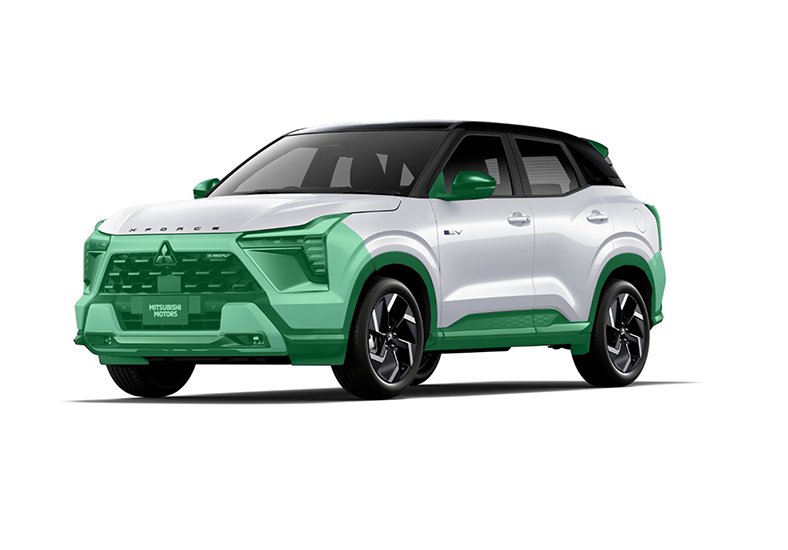

Exterior
-
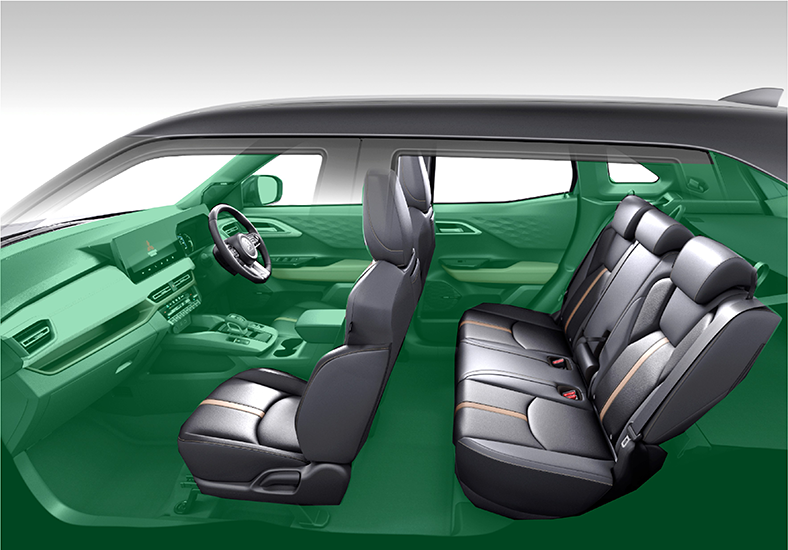

Interior
Promote recycling of end-of-life vehicles
MITSUBISHI MOTORS Group encourages the recycling of endof-life vehicles to reduce the environmental impact of waste from these vehicles. In Japan, the European Union (EU) and other regions, we promote recycling in accordance with the automobile recycling laws of each country. We comply carefully with the evolving automobile recycling laws that are being introduced in emerging countries in Asia.
The Environmental Targets 2030 identify the reuse of batteries used in electrified vehicles as one item to be addressed. From the perspective of conserving resources, we are undertaking initiatives to utilize used batteries.
Reuse of Batteries Used in Electrified Vehicles
Used electrified vehicle batteries retain sufficient storage capacity to make them useful for other applications, so from the perspective of conserving resources we are working to effectively reuse electrified vehicle batteries. To ensure these batteries can be effectively used for storage, we are conducting verification using a large-scale rooftop solar power system at the Okazaki Plant and built a power storage system that employs used batteries from the “OUTLANDER PHEV” (previous model).
In January 2023, we installed equipment for the demonstration of two concepts employing used batteries in conjunction with quick chargers and bidirectional chargers at the Okazaki Plant, and we have begun the demonstration.
Going forward, we will work with energy storage equipment manufacturers to introduce these systems at Group’s sales companies’ dealers and in other locations.
In addition, with MIRAILABO Co., Ltd., we have developed self-directed lights that reuse batteries from electrified vehicles.
Our self-directed lights store solar power generated during the day in used batteries from electrified vehicles and use that power to illuminate LED lights at night. In FY2022 and FY2023, we installed and performed verification testing of 24 selfdirected lights at our Okazaki Plant, Mizushima Plant, Kyoto Plant, and Tokachi Research & Development Center. In March 2025, we began selling these self-directed lights, with the first unit installed at the Okazaki City Social Welfare Council Service Center.
In addition, in Japan, Europe and North America, the Group has begun creating a system for collecting used batteries. The aim is to develop recycling technologies for and to properly dispose of batteries for electric vehicles and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles.
Response to Automobile Recycling Laws in Japan
Since the End-of-Life Vehicle Recycling Law was enacted in Japan in 2005, we have been accepting used automobile shredder residue (ASR*2), airbags, and fluorocarbons for recycling.
Regarding ASR recycling, we participate in ART*3 in order to jointly process ASR. As a result of the creation of new processing facilities and other measures, the ASR recycling rate in FY2024 was 96.7%, substantially above the statutory standard of 70% in effect since 2015. We will continue to develop new recycling facilities to ensure the stable processing of ASR.
We outsource the treatment of airbags and fluorocarbons to the Japan Auto Recycling Partnership (JARP).
In FY2024, our effective recycling rate for end-of-life vehicles*4 exceeded 99%, surpassing the government’s stipulated effective recycling rate of 95%.
- Automobile shredder residue
- Automobile Shredder Residue Recycling Promotion Team established by 12 companies, including Nissan Motor Co., Ltd., Mazda Motor Corporation and MITSUBISHI MOTORS.
- Effective recycling rate: The recycling rate for end-of-life vehicles. The ratio recycled in the dismantling and shredding process is approximately 83% (cited from the materials of the 3rd joint meeting of the Automobile Recycling Expert Committee of the Central Environmental Council and the Automobile Recycling Working Group of the Industrial Structure Council in May 2003), multiplied by the remaining ASR ratio of 17% and the ASR recycling rate for the relevant fiscal year.
Recycling Promotion in the EU
Response to the EU’s Directive on the Recycling of End-of-Life Vehicles
In the EU, in accordance with the End-of-Life Vehicles Directive*5 established in 2000, automobile manufacturers or importers must accept and recycle end-oflife vehicles.
The Group has built a system of acceptance and recycling in line with the actual situation of EU member countries centering on our European subsidiary Mitsubishi Motors Europe B.V. (MME).
- “Directive of the European Parliament and of the Council on End-of- Life Vehicles”
Provision of Dismantling Information
In the EU, automobile manufacturers must provide dismantling information for new model vehicles to treatment operators. We provide such information on a timely basis by using the International Dismantling Information System (IDIS) jointly developed by automobile manufacturers.
Response to the EU’s Directives on Approval for Vehicle Models for Recyclability
In the EU, satisfying the minimum 95% recyclability rate is a requirement for the type approval of vehicle models, and the Group has established a system that satisfies the requirements of this directive. MITSUBISHI MOTORS Group vehicles sold in the EU meet the requirements of the directive under this system.
Initiatives to Reduce Waste Generation and Reuse Resources in Production Activities
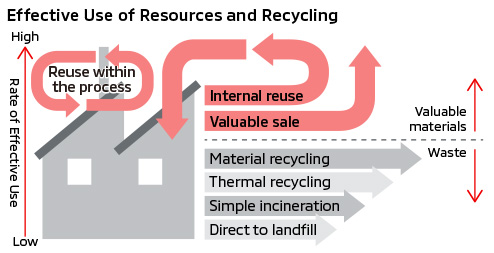
We are working to reduce the amount of waste generated through manufacturing by improving its production processes. As for the generated waste, we reduce treatment costs and continue to improve the sorting and treating methods to utilize it as resources.
Responses Related to the Plastic Resource Circulation Act
In FY2024, we achieved a recycling rate of 100% for industrial waste from products using plastic (hereinafter "waste plastic").
We will continue to promote the recycling of waste plastic and maintain this 100% recycling rate*6.
Volume of industrial waste from products using plastic and
recycling rate (Okazaki Plant, Mizushima Plant, Kyoto Plant)
| FY2023 | FY2024 | |
|---|---|---|
| Volume of waste | 1,796t | 1,973t |
| Recycling rate | 97% | 100% |
- Recycling rates were calculated using the recycling rate calculation method specified by the Japan Automobile Manufacturers Association
TOPICS
Reducing Waste Volume by Upgrading Sludge Dewatering Equipment (Okazaki Plant)
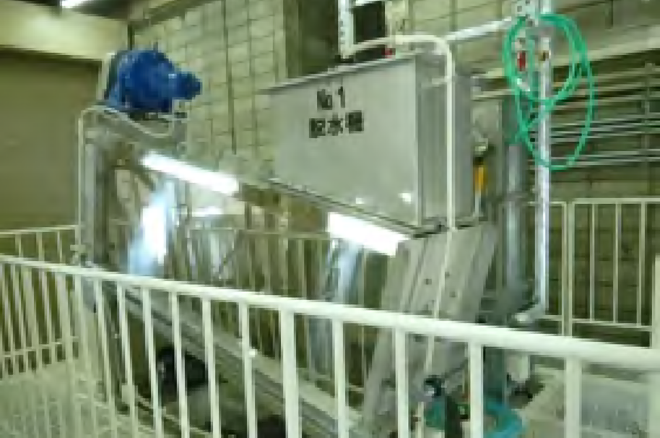

Installed screw-type sludge dewatering equipment
With regard to waste generated by our business activities, to achieve the goal set in Environmental Targets 2030 of “zero direct landfill waste (less than 0.5%),” we are working to reduce waste generated in external and reuse resources. In FY2024, our management target companies achieved zero direct landfill waste (less than 0.5%).
Achievement of Zero Direct Landfill Waste
With regard to waste generated by our business activities, to achieve the goal set in Environmental Targets 2030 of “zero direct landfill waste (less than 0.5%),” we are working to reduce waste generated in external and reuse resources. In FY2023, our management target companies achieved zero direct landfill waste (less than 0.5%).