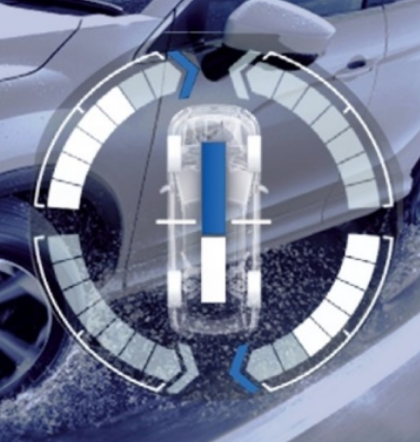
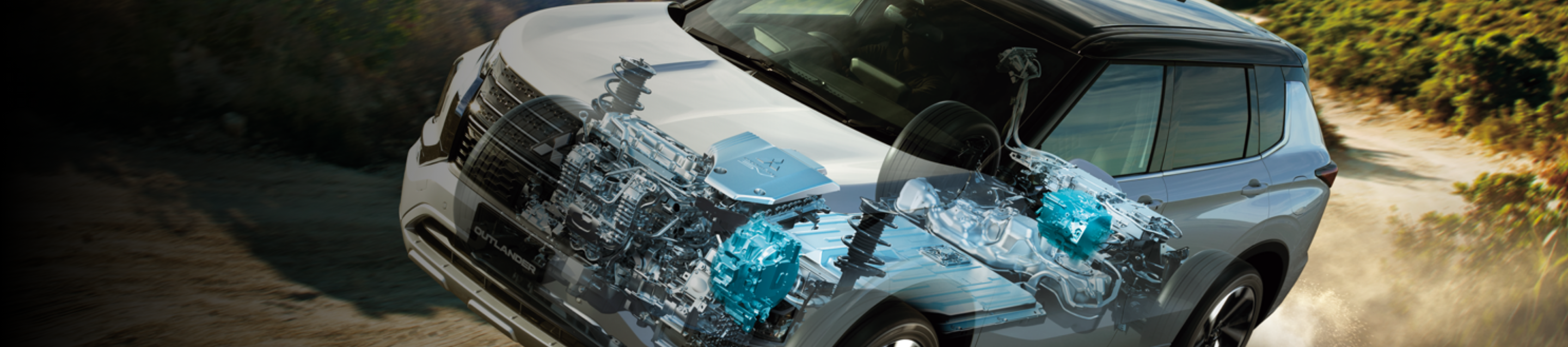
MITSUBISHI MOTORS Technology
We are continually refining our technology to achieve carbon neutrality, protecting both the planet and our way of life. Our goal is to deliver vehicles that customers can enjoy and drive with confidence, ensuring a safe return from every adventure, while bringing excitement to everyone on board.
Among our many innovations, the following are the core technologies that define Mitsubishi Motors-ness.