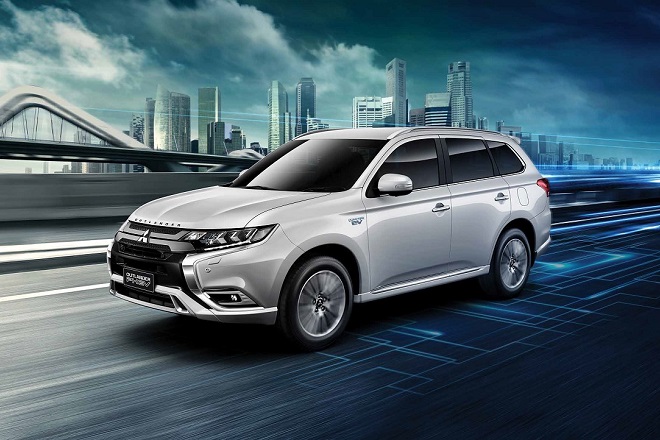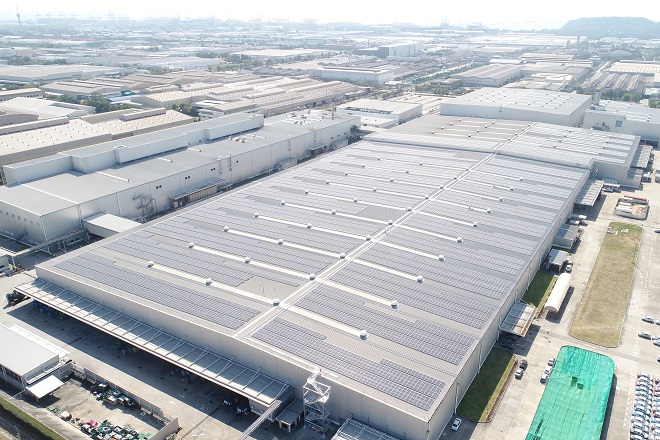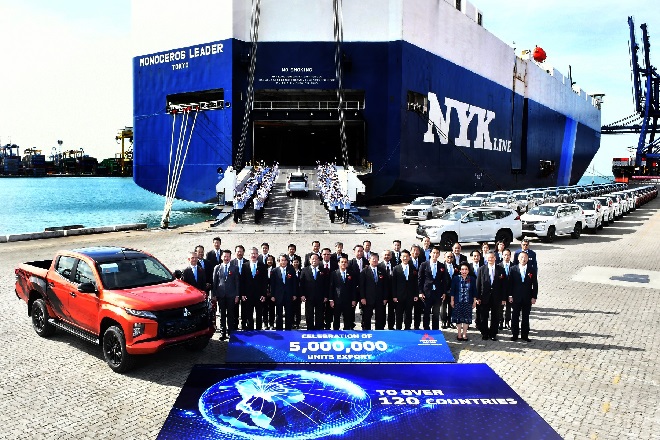
Company History
Presented here is Mitsubishi’s journey in the
automobile industry since the company’ establishment.

Company History
Presented here is Mitsubishi’s journey in the
automobile industry since the company’ establishment.

View the history
of past cars
1870
Tsukumo Shokai (later Mitsukawa Shokai) was founded by the Tosa Clan, positioning Yataro Iwasaki as the manager.
1873
Yataro Iwasaki changed the company’s name from Mitsukawa Shokai to Mitsubishi Shokai, and became the company’s president.
1875
Mitsubishi Shokai changed its name to Mitsubishi Kisen Kaisha.
Mitsubishi Kisen Kaisha changed its name to Yubin Kisen Mitsubishi Kaisha.
1885
Yanosuke Iwasaki founded Mitsubishi Sha (later Mitsubishi Goshi Kaisha), and became the company’s president.
1893
Hisaya Iwasaki became president of Mitsubishi Goshi Kaisha.
1914
Mitsubishi registered its trademark (the three-diamond symbol).
Mitsubishi registered its trademark (the three-diamond symbol).
The symbol “![]() ” originates from the three-diamond emblem that Tsukumo Shokai used for its ship’s flag since it took over the shipping business from the Tosa Clan in October 1870.
” originates from the three-diamond emblem that Tsukumo Shokai used for its ship’s flag since it took over the shipping business from the Tosa Clan in October 1870.
It is said that the emblem is derived from the three stacked rhombuses which was the crest of the Iwasaki family, and the three oak leaves which was the crest of the lord of the Tosa Clan, the Yamauchi family.
The diamonds used to be required around 30-degree angle and then was changed to have 60-degree angle when the symbol was updated to be the present form in 1910. In March 1914, Mitsubishi Goshi Kaisha filed a trademark application with the Patent Office, and the symbol was registered as the company’s trademark in June of the same year.
Later on, as the company diversified its business, the use of its new enterprises’ name “Mitsubishi” as well as the three-diamond symbol spread. MITSUBISHI MODEL A, Japan’s first mass-produced passenger car completed in November 1918, also bore this emblem on its radiator grille.
Prev
Next
1916
Koyata Iwasaki became president of Mitsubishi Goshi Kaisha.
1917
The Shipbuilding Division of Mitsubishi Goshi Kaisha becomes the independent company Mitsubishi Shipbuilding Co., Ltd.(later Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.)
1920
Mitsubishi Internal Combustion Engine Mfg. Co., Ltd. established Nagoya Plant.
Mitsubishi Internal Combustion Engine Mfg. Co., Ltd. established Nagoya Plant.
Mitsubishi Internal Combustion Engine Mfg. Co., Ltd. (later Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.) established the Nagoya Works (later Oe Plant) on the land reclaimed from the sea beyond Higashitsukiji, Minami Ward, Nagoya, Aichi Prefecture (current address: Oe-cho, Minato Ward, Nagoya) to manufacture aircraft fuselages. After World War II, the plant switched to the manufacture of motor vehicles in order to meet private-sector demand. The plant began manufacturing Silver Pigeon scooters in 1946, and four-wheel-drive vehicle Mitsubishi Jeeps in 1952.
In August 1977, Mitsubishi Motors established its first plant, Nagoya Motor Vehicle Works - Okazaki Plant, in Hashime-cho, Okazaki, Aichi Prefecture. The company manufactured motor vehicles at this plant and the Oe Plant in the Nagoya area since, but in 2001, it closed down the Oe Plant.
In October 2016, Nagoya Works was renamed Okazaki Plant, and today, the plant manufactures automobiles, mainly sport utility vehicles (SUVs).
The Nagoya area has also been the development base covering from basic research to product development. The Okazaki test track was completed in 1962, and the Mitsubishi Motors Technical Center (currently Research & Development Center) was established in Hashime-cho, Okazaki, Aichi Prefecture in 1969.
Furthermore, in April 2012, the EV Research & Development Center was established for electric vehicle development in Nikki-cho, Okazaki, Aichi Prefecture.
Prev
Next
1943
Mizushima Aircraft Plant (currently Mizushima Plant) established by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Mizushima Aircraft Plant (currently Mizushima Plant) established by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. established the Mizushima Aircraft Plant in the area beyond the Takahashi estuary (currently Mizushima Kaigan Dori in Kurashiki) in Tsurajima-cho, Asakuchi, and Fukuda-son, Kojima, Okayama Prefecture, to manufacture aircraft fuselages. After World War II, the plant switched to the manufacturing of motor vehicles in order to convert their technology to civilian use. The production of the three-wheel cargo carrier Mizushima was started in 1946, the mid-sized truck Jupiter in 1959, and the lightweight commercial vehicle Mitsubishi 360 in 1960.
In June 1999, Mitsubishi Motors changed the name of the plant from Mizushima Motor Vehicle Works to Mizushima Plant, which currently produces cars and engines, mostly light automobiles, as well as electric vehicles.
Prev
Next
1944
Kyoto Device Manufacturing Works (currently Kyoto Plant - Kyoto) established by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Kyoto Device Manufacturing Works (currently Kyoto Plant - Kyoto) established by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. established Kyoto Device Manufacturing Works in Uzumasa, Kyoto (currently Uzumasa Tatsumi-cho, Ukyo Ward, Kyoto) to produce aircraft engines. After World War II, the plant switched to the manufacture of car engines and transmissions to civilian establishment. The production of the GB 38 gasoline engine was started in 1946 and the KE 5 diesel engine (“KE” stands for Kyoto Engine) in 1949.
In December 1979, after the founding of Mitsubishi Motors, the company established Kyoto Works - Shiga Plant in Kosei-cho, Koga, Shiga Prefecture (currently Kosuna-cho, Konan). Today, the Kyoto and Shiga Plants produce car engines.
Kyoto Works was renamed Powertrain Works in June 2003, and then renamed again Kyoto Works in April 2017.
Prev
Next
1949
Established a truck and bus distributor, Fuso Motors Sales Co., Ltd.
1950
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. split into 3 companies.
1952
Companies including the three Mitsubishi Heavy Industries companies moved their headquarters to Marunouchi in Chiyoda City, and began to use Mitsubishi’s corporate name and its three-diamond symbol again.
1954
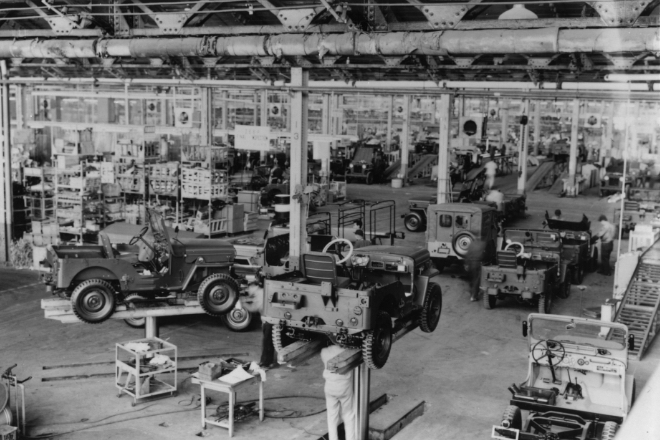
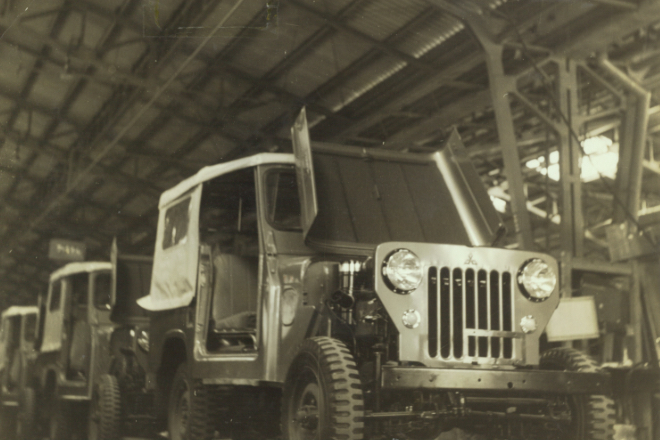
Established Ryowa Motor Sales Company (later Shin Mitsubishi Motor Sales Company) as a distributor for domestically manufactured jeeps.
Established Ryowa Motor Sales Company (later Shin Mitsubishi Motor Sales Company) as a distributor for domestically manufactured jeeps.
In July 1952, Shin Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Co., Ltd. (the predecessor of Mitsubishi Motors) and Willys-Overland Motors in the United States signed an outsourcing agreement for knock-down assembly of Jeep. The first J1 Mitsubishi Jeep was completed in February the following year.
In July of the same year, Shin Mitsubishi concluded technical assistance and sales agreements with Willys-Overland to acquire the licenses to manufacture and sell Jeep in Japan. Following this license acquisition, Shin Mitsubishi and Kurashiki Rayon Co., Ltd. (currently Kuraray Co., Ltd.) jointly founded Ryowa Motor Sales Company as a seller of all the Jeep vehicles manufactured in Japan in May 1954. In July 1956, the production of the Japan made Jeeps was launched.
Asides from the Mitsubishi Jeeps, Ryowa Motor Sales Company began to sell the Jupiter, Rosa, and Mitsubishi 500. In May 1963, the company was renamed Shin Mitsubishi Motor Sales Company, and sold all lines of motor vehicles produced by Shin Mitsubishi Heavy Industries.
Prev
Next
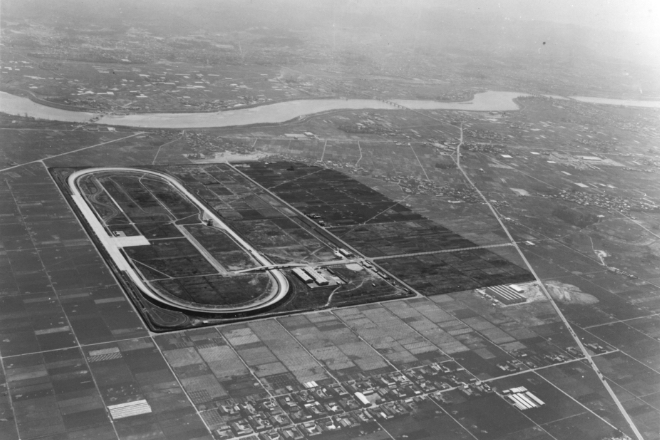
1962
Okazaki Test Course completed at Nagoya Plant.
1964
The three Mitsubishi Heavy Industries companies merged to form the new Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Established Mitsubishi Motor Sales Company.
Established Mitsubishi Motor Sales Company.
After World War II, Mitsubishi was broken up into three heavy industry businesses. In June 1964, these three merged to form new Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. This merger integrated the production of large- and mid-sized trucks and buses by Mitsubishi Nippon Heavy Industries and scooters, light motor vehicles, passenger cars, mid- and small-sized trucks and buses by Shin Mitsubishi Heavy Industries under the umbrella of one brand.
Following this integration of the production departments, Mitsubishi Fuso Motors and Shin Mitsubishi Motor Sales Company explored the possibility of amalgamation to establish a large-scaled motor sales company handling all types of vehicles including scooters, light motor vehicles, and large trucks and buses. In June 1964, the two businesses’ board of directors approved the resolution to conclude a merger agreement, which specified that Mitsubishi Fuso Motors shall be the surviving company in the merger, and that the company’s trade name shall be changed to Mitsubishi Motor Sales Company.
The notice of the merger was submitted to the Japan Fair Trade Commission in August 1964, and the new company was launched in October.
Prev
Next
1965
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. acquired shares in UDMI of Thailand.
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. acquired shares in UDMI of Thailand.
Exports of Mitsubishi vehicles to Thailand began with large buses in 1952. In August 1961, Sittipol Motor Company (SMC) was established with local capital as a sales company for imported Mitsubishi vehicles. In the beginning, the three-wheeled light vehicle Leo was exported. The vehicles sold by SMC gradually increased in variety and number, including passenger cars and mid-sized trucks.
In the 1960s, Thailand promoted local assembly of vehicles to invite foreign capital, as an alternative policy for imported cars. Following this move, United Development Motor Industries Co., Ltd. (UDMI) was established with local capital in October 1964. Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. began equity participation in UDMI the following year, and in June 1966, UDMI launched the production of Mitsubishi vehicles as the first local Mitsubishi car manufacturer overseas.
In December 1973, Mitsubishi Motors began equity participation in SMC that served as its local sales company. It operated its business in Thailand jointly with the local companies, with SMC being their seller and UDMI the manufacturer. These two companies merged in January 1987 to form MMC Sittipol Co., Ltd (MSC; located in Bangkok, Thailand).
In November 2003, to enhance sales and marketing strategies by unifying the companies’ names, MSC was renamed Mitsubishi Motors (Thailand) Co., Ltd. (MMTh), and has been in effect since then.
Prev
Next
1966
Dealers nationwide were crowned with the title of “Mitsubishi Motor Sales” in their corporate names.
1967
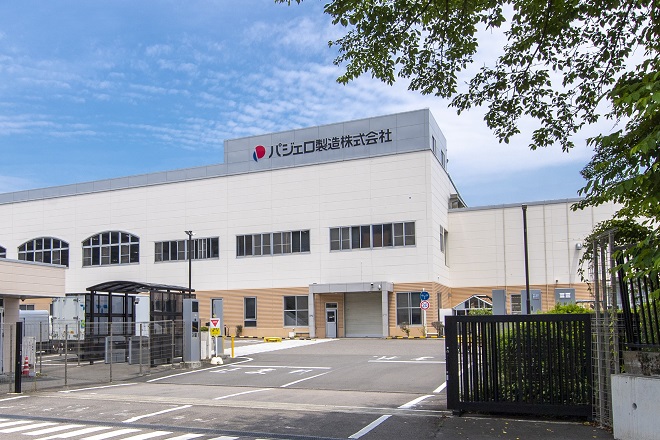
Production of jeeps fully outsourced to Toyo Machinery Co., Ltd. (currently Pajero Manufacturing Co., Ltd.)
Production of jeeps fully outsourced to Toyo Machinery Co., Ltd. (currently Pajero Manufacturing Co., Ltd.)
The Mitsubishi Jeep had been manufactured by Shin Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, our predecessor, since 1953. Later, the production was later fully outsourced to Toyo Machinery Co., Ltd. (then located in Kita Ward, Nagoya) as part of the streamlining project at Nagoya Motor Vehicle Works.
Toyo Machinery relocated its plant to Sakahogi-cho, Gifu Prefecture in September 1976. The company integrated manufacturing of Pajero, which originated from the Mitsubishi Jeep, in February 1982. The company changed its name to Pajero Manufacturing Co., Ltd. in July 1995.
Prev
Next
1968
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. completed the construction of the main building of Mitsubishi Kyoto Hospital.
1969
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. set up the division for its automobile business.
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. moved the division for its automobile business to Shiba, Minato City.
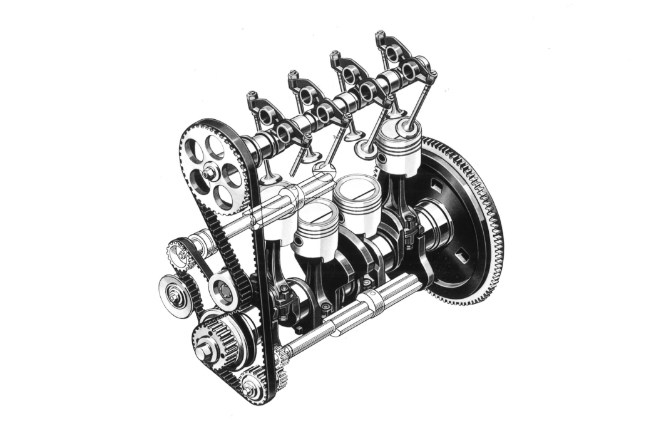
Launched the production of 4G3 model (Saturn Engine).
Launched the production of 4G3 model (Saturn Engine).
The 4G3 Saturn engines use Mitsubishi’s first overhead camshaft (OHC) mechanism for water-cooled in-line four cylinder gasoline engines, which were designed to yield high performance while controlling exhaust fumes that was becoming a social issue. This product line was named Saturn, following the precedents of the names “Venus” and “Mars” given to the aircraft engines manufactured during World War II.
The 1.3 liter 4G30 and 1.5 liter 4G31 models were installed in the first-generation Colt Galant launched in December 1969. The 1.6 liter 4G32 model was added in the following year. Galant GTO-MR was installed with a dual overhead camshaft (DOHC) engine for high output of 125 ps/6,800 rpm.
In 1973, when emission regulations were tightened, Mitsubishi was one step ahead of its competitors, having started producing engines that met the regulations since in 1972. These engines were of the 4G3 line. The engine variation expanded from the 2.0 liter 6G34 model with six cylinders for the Debonair as well as the 1.4 liter 4G33, 1.7 liter 4G35, and 1.8 liter 4G37 models, and were manufactured for decades.
- Years manufactured: 1969–1996
- Total production: 4,210,000
- Displacement: 1,300 cc–2,000 cc
- Models of cars equipped with these engines: Colt Galant, Galant GTO, Lancer, Debonair, Galant Σ
Prev
Next
Automotive research and development center was set up in Nagoya plant.
The soccer team of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. won the Japan Soccer League for the first time.
1970
Mitsubishi Motors Corporation was founded.
Mitsubishi Motors Corporation was founded.
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. advanced establishing a department dedicated to its automobile business in order to adapt to the age of fully internationalized automotive industries that were brought into reality by capital account liberalization. In February 1970, the company entered into a master agreement for a joint venture with Chrysler. With this agreement, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries transferred its automobile business department to the new venture. On April 22 of the same year, Mitsubishi Motors Corporation was established as a new company wholly owned by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries. Chrysler also began equity participation in this new venture in the form of a capital increase through third party allotment of new shares.
Moreover, with the business transfer agreement signed on the same day, the sales operations for the automobile business along with some of the plants owned by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries were transferred to Mitsubishi Motors as of midnight on June 1, 1970.
As soon as Mitsubishi Motors was launched, Mitsubishi vehicles were exported to North America and other regions through Chrysler’s sales network. In October of the same year, a US distributorship agreement (USDA) was executed with Chrysler, and then a Canada distributorship agreement with Chrysler Canada in December. In January of the following year, the Colt Galant, which Chrysler acclaimed, was launched as the Dodge Colt in the west coast of North America.
In May 1971, a small market distributorship agreement was signed with Chrysler International S. A. (CISA, based in London) to launch sales in markets other than North America through CISA.
Mitsubishi’s automobile business in overseas markets, which was one of the major objectives of the establishment of Mitsubishi Motors, started to off.
Prev
Next
Concluded an agreement with CMC to provide assistance on enhancing domestic production in Taiwan.
Concluded an agreement with CMC to provide assistance on enhancing domestic production in Taiwan.
Mitsubishi vehicles had already been exported to Taiwan since 1934. In October 1970, as its first overseas business operation project, Mitsubishi Motors oncluded an agreement with China Motor Corporation (CMC) in Taiwan to provide assistance on enhancing domestic production. The knock-down production of large trucks and the Delica trucks began in December 1973, and the makes of vehicles produced under the agreement gradually increased.
Since its group company Yulon Motor jointly manufactured mainly passenger cars with Nissan Motor Corporation, CMC only dealt with commercial vehicles by Mitsubishi. Yet in 1985, CMC launched the Minica called “Towny” with an 800-cc engine and released it as the first ever passenger car.
As CMC and Mitsubishi Motors worked closely together, Mitsubishi Motors and Mitsubishi Corporation began equity participation in CMC in 1986. CMC continues to manufacture and sell Mitsubishi vehicles in Taiwan today.
Prev
Next
100th anniversary of Mitsubishi Group.
1971
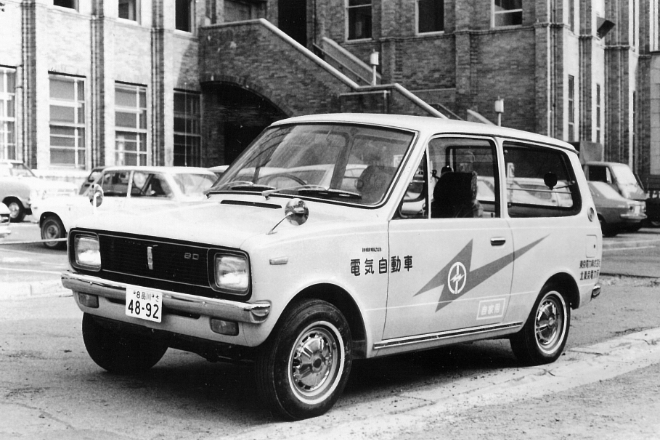
10 Minica Van EVs were delivered to Tokyo Electric Power Company.
10 Minica Van EVs were delivered to Tokyo Electric Power Company.
In October 1966, Tokyo Electric Power Company and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. entered into an agreement for entrusted research titled “Prototype and various tests of electric vehicles by improving existing batteries.” Mitsubishi Electric Corporation and Japan Storage Battery Co., Ltd. (currently GS Yuasa Corporation) also joined. The project explored potential electric vehicles (EV) based on the Minica Van, and in December 1969, the EV Minica Van (E12X model) was launched.
This EV had great accelerating power and climbing ability, demonstrating its capability that was as good as gasoline cars. It enjoyed a high reputation in a test-drive at Tokyo Electric Power Company’s Tokyo office.
The E12 model, an upgraded version of the E12X model, boasted the maximum speed of 80 km per hour and cruising distance of 70km (30km/h at constant speed). 10 E12 Minica Vans were delivered to Tokyo Electric Power as company cars.
Prev
Next
Launched the production of 4G4 model (Neptune Engine).
Launched the production of 4G4 model (Neptune Engine).
The 4G4 Neptune engines were water-cooled in-line four cylinder gasoline engines inheriting the OHV style. The 1.4 liter 4G41 model was installed in Galant FTO that was launched in November 1971. The 1.2 liter 4G42 model was later added for the Lancer, yet the production discontinued in 1981.
- Years manufactured: 1971–1981
- Total production: 520,000
- Displacement: 1,200 cc–1,400 cc
- Models equipped with these engines: Galant FTO, Lancer
Prev
Next
Entered into equity alliance with Chrysler.
Entered into equity alliance with Chrysler.
In February 1971, Chrysler requested Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. to change method to equity participation based on the master agreement for a joint venture (executed in February 1970). In May of the same year, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries signed a second master agreement (an updated version of the first agreement), according to which the company switched over to equity investments in three stages from a one-time investment.
On the day this agreement was signed, Chrysler submitted the notice of acquiring shares in the new company (Mitsubishi Motors) to the Japanese government for approval. In September of the same year, Mitsubishi Motors, with the capital increased through third party allotment of new shares, issued 527,700 shares (face value of 10,000 yen) to start over as a motor vehicle company capitalized at 35.177 billion yen, with both Mitsubishi Heavy Industries holding 85 percent of the shares and Chrysler 15 percent.
The master agreement between Mitsubishi Heavy Industries and Chrysler continued for 14 years until it was terminated by the two companies in June 1985.
Prev
Next
1972
The soccer team of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. won the Emperor’s Cup JFA Japan Football Championship for the first time.
Kyoto Plant Rugby Team won the 24th Japan Company Rugby Football Championship for the first time.
Mitsubishi Rented Car Corporation (later Mitsubishi Auto Leasing Corporation) was founded.
Acquired shares in CPC of the Philippines.
Acquired shares in CPC of the Philippines.
Mitsubishi vehicles had been exported to the Philippines since 1955. Nissho Iwai Corporation (currently Sojitz Corporation) set up a distributor, and they began knock-down production afterwards.
After its establishment, Mitsubishi Motors joined Nissho Iwai and a local business in equity participation in Chrysler Philippines (CPC; Chrysler’s Philippine office) at the request of Chrysler and Chrysler International S.A. (CISA). They assembled and sold Colt Galant, Lancer, and Minica, among others at CPC.
When Chrysler completely withdrew its business from the Philippines, CPC’s name was changed to Canlubang Automototive Resources Corporation (CARCO), and the company was turned into a joint venture funded by Mitsubishi Motors, Nissho Iwai, and the local business.
In the 1980s, with the political instability that led to economic turmoil in the Philippines, demand for automobiles dipped. Consequently, in February 1987, following changes the Philippine government made to its automotive industry development plan in the same year, Mitsubishi Motors and Nissho Iwai jointly established a new company called Philippine Automotive Manufacturing Corporation (PAMOCR; located in Cainta, the Philippines).
Aiming to clarify, domestically and internationally, that the joint venture produced and sold Mitsubishi vehicles, PAMOCR was renamed to include “Mitsubishi” in its trade name. In August 1996, the company made a start as Mitsubishi Motors Philippines Corporation (MMPC), and it has served as our vehicle production and sales base to date.
Prev
Next
Kawasaki Baseball Team entered the 43rd Intercity Baseball Tournament and came second.
Launched the production of 4G5 model (Astron Engine).
Launched the production of 4G5 model (Astron Engine).
The 4G5 Astron engines were water-cooled in-line four cylinder gasoline engines, essentially the same as those of the 4G3 model, yet one size bigger being a 2-liter-class engine. In January 1973, the 2.0 liter 4G52 model was installed in the Galant GTO. The 1.8 liter 4G51 model was added to the lineup in May of the same year, the 2.4 liter 4G53 model in August 1974, and the 2.6 liter 4G54 model in June 1976. They were installed in Debonair, New Galant, Canter, and Rosa, among others.
In February 1975, Galant GTO with the 4G52 Astron 80 engine was launched. The engine of this four-cylinder model used a silent shaft system applied to the 4G52 engine, achieving quietness equivalent to an 8-cylinder. To pursue an ideal engine for the 1980s, we collectively named engines that used the silent shaft system as ’80 engines.
To meet the demand of the resource and energy conservation age, Mitsubishi Motors completed the development of the 2.4 liter 4D55 model in May 1980. This model is a diesel version of the 4G5 model to serve as Japan’s first diesel engine with a turbo designed for passenger cars, and it was installed in the Galant, and Eterna Σ and Λ. The 4D55 model was widely adopted for commercial vehicles afterwards, including Pajero and Delica. Then the 2.5 liter 4D56 model, Japan’s first engine with a turbocharger for passenger cars, was suited in May 1986, and in October 1988, a turbo version with an intercooler was added for the Pajero.
- Years manufactured: 1972–2013
- Total production: 5,220,000
- Displacement: 2,000 cc–2,600 cc
- Models equipped with these engines: Galant Σ, Debonair, Pajero
Prev
Next
1973
Founded ATC in the Philippines.
Founded ATC in the Philippines.
In 1971, following the Progressive Car Manufacturing Program (PCMP) issued by the Philippine government, aiming to increase the percentage of domestically produced cars and to acquire foreign currency, Mitsubishi Motors, Chrysler Philippines (CPC), and Nissho Iwai Corporation (currently Sojitsu Corporation) established the joint venture Asian Transmission Corporation (ATC; located in Canlubang, the Philippines) for parts manufacturing. In July of the same year, the construction of a plant began in Manila. The manufacturing of manual transmissions started in 1974, of engines in 1991, and of axles in 1995.
In 1998, with demand for these products growing in the Philippines and our export to the ASEAN member states and other Asian countries/regions increase, the production was relocated to a new plant built in an industrial park near the original plant in order to boost manufacturing capacity.
In June 2014, Mitsubishi Motors bought shares of ATC from Sojitsu and the manufacturing and sales company Mitsubishi Motors Philippines Corporation (MMPC) to hold 90 percent of shares in ATC, aiming to strengthen its production facility. Vehicle transmissions are manufactured by ATC in the Philippines.
Prev
Next
Founded MKM in Indonesia.
Founded MKM in Indonesia.
The export of Mitsubishi vehicles to Indonesia began in 1958. There were distributors and knock-down production bases for the Mitsubishi Jeep, Delica, and mid-sized trucks, yet it was an alliance with Mitsubishi Corporation and the local partner PT Krama Yudha (KY) that provided a foothold needed for the full launch of the company’s automobile business in Indonesia.
To adapt to the policy on domestic manufacturing in Indonesia, Mitsubishi Motors and Mitsubishi Corporation established PT Mitsubishi Krama Yudha Motors and Manufacturing (MKM) for the production of components for locally manufactured vehicles as a joint venture with KY in 1973. The production began in 1975.
The manufacturing of motor vehicles was outsourced to PT Krama Yudha Ratu Motors (KRM), which was wholly funded by KY and began the production of the Colt and mid-sized and large trucks in 1975. Later, Mitsubishi Motors, Mitsubishi Corporation, and KY established PT Mitsubishi Motors Krama Yudha Indonesia (MMKI; located in Bekasi, Indonesia) and began motor vehicle production in April 2017.
Furthermore, intending to restructure the marketing business, PT Krama Yudha Tiga Berlian Motors (KTB), which had sold Mitsubishi vehicles in Indonesia since 1973 under the distributorship agreement with Mitsubishi Motors, was split brands of Mitsubishi Motors and of Mitsubishi Fuso Truck and Bus Corporation. Then Mitsubishi Motors, Mitsubishi Corporation, and KY jointly established PT Mitsubishi Motors Krama Yudha Sales Indonesia (MMKSI; located in Jakarta, Indonesia) as a sales company exclusively for the Mitsubishi Motors brands in April 2017. In the Indonesian market, the Mitsubishi Motors brands’ vehicles are sold via MMKSI.
Prev
Next
Concluded an agreement to provide technical assistance for the 4G36 model engine to Hyundai Motor Company.
Acquired shares in SMC of Thailand.
1975
Established Meiko Motor Pool in Nagoya port in Aichi Prefecture.
1976
The “silent shaft” system won the Technological Development Award of the Society of Automotive Engineers of Japan, Inc.
The “silent shaft” system won the Technological Development Award of the Society of Automotive Engineers of Japan, Inc.
Most passenger cars used four-cylinder engines at the time. These engines were more resource- and energy-efficient and lower-cost than six- and eight-cylinder and rotary engines, whereas they were at a disadvantage in terms of the level of vibration and noise. It was already known at the time that vertical vibrations could be reduced by two balancer shafts counter-rotating at twice the speed of the crankshaft that were built in the cylinder block. Mitsubishi Motors strived to further control the level of vibration, and successfully developed the “silent shaft” system that dramatically reduced vibrations at low and high speed by placing the balancer shaft that rotated into the same direction as the crank shaft in a further upward position.
This silent shaft system made four-cylinder engines as quiet as eight-cylinder engines. It was installed in the 2 liter 4G52 Astron engine, and built in New Galant GTO as Astro 80 Engine.
In 1976, the silent shaft system won the Technological Development Award of the Society of Automotive Engineers of Japan, Inc.
The "Silent Shaft" system was also licensed to European manufacturers (Porsche, Volvo, Saab).
Prev
Next
Kyoto Plant Rugby Team won again in the 28th Japan Company Rugby Football Championship.
Began using the MM symbol for the front emblem.
Began using the MM symbol for the front emblem.
Mitsubishi Motors designed a new logo using the first letters of its name. Galant Σ that bore this “MM” symbol made its debut.
Since the motor vehicles Mitsubishi Motors manufactured and sold were designed to bond with users, the new symbol aimed to further highlight the unique images of Mitsubishi vehicles, each bearing the signature of Mitsubishi Motors.
The “mighty red” (left), our then-corporate color, represented sincerity and vitality, and the “lofty blue” (right) youth and fulfilling futures. The emblem was also used for public relations materials.
Mirage II and Lancer Fiore that were launched in February 1982 started using the new symbol “MMC” for the front emblem, followed by Tredia and Cordia launched the following month. This symbol was created to represent all Mitsubishi Motors vehicles.
In May 1992, taking into account a full upgrade to Galant and Eterna, the MMC logo used in ads and promotions, stores, and car bodies was replaced with the three-diamond logo.
Prev
Next
Introduced the MCA-JET system engine.
Introduced the MCA-JET system engine.
The Mitsubishi Clean Air-Jet Controlled Super Lean Combustion System (MCA-JET) was adopted for the engines of all Mitsubishi passenger cars, ranging from 500-cc engines (Minica 5) to 2.6-l engines (Debonair). MCA-JET delivered fuel efficiency and high performance, particularly in response to the age of resource and energy conservation. The engines with this pioneering MCA-JET met the 1978 motor vehicle emission control requirements, which were considered the world’s toughest at the time, before any other companies did.
MCA-JET, is short for Mitsubishi Clean Air-jet-controlled super lean combustion system, and has a jet valve, in addition to an intake/exhaust valve, in the combustion chamber. This empowers super lean air-fuel mixture or air to eject into a certain direction at the right time for the driving condition, enabling efficient combustion at the optimal air-fuel ratio. The MCA-JET system helped improve fuel efficiency and make exhaust gas cleaner.
Prev
Next
1977
Launched the production of 4G1 model (Orion Engine).
Launched the production of 4G1 model (Orion Engine).
The 4G1 Orion engines were small and lightweight engines (water-cooled in-line four cylinder gasoline engines) designed for greater efficiency with less displacement than the 4G3 engines to meet the demands of the energy conservation age after the oil crisis in 1973. The 1.3 liter 4G11 model was installed in Lancer in May 1977. This engine used the Mitsubishi Clean Air-Jet Controlled Super Lean Combustion System (MCA-JET), and it met Japan’s motor vehicle emission control requirements, which were considered the world’s toughest at the time, one year before they were enforced in 1978.
The 1.4 liter 4G12 model was installed in the Mirage launched in March 1978. With the full upgrade of the Mirage in October 1983, the 1.3 liter 4G13 and 1.5 liter 4G15 models with an enlarged bore were added.
In February 1982, the 4G12 model that used the modulated displacement technology was installed in Mirage II.
Furthermore, the 4G15 model with Mitsubishi Vertical Vortex (MVV) was installed in the new Mirage and Lancer that were launched in October 1991.
The 4G19 model installed in the new Colt that was launched in November 2002. The newly developed 1.3 liter DOHC MIVEC (with variable valve timing mechanism) engine combined with CVT (continuously variable transmission) delivered good engine response for a smooth ride. In its 10-15 mode, the engine accomplished the fuel efficiency of 20 km per liter (for a 1.3-liter car optionally equipped with the model), delivering the highest-level fuel efficiency for this vehicle class even in urban areas. Due to this performance, cars with this engine were certified as “super low-emission vehicles” that successfully cut 75 percent of exhaust fumes to meet the emission control requirements in 2000. The engine also met the 2010 fuel efficiency standards, and all cars equipped with this model became eligible for green tax breaks.
- Years manufactured: 1977–2014
- Total production: 9,680,000
- Displacement: 1,200 cc–1,600 cc
- Models equipped with these engines: Lancer, Mirage, Colt
Prev
Next
Hosted Mitsubishi Galant Tournament.
Hosted Mitsubishi Galant Tournament.
Mitsubishi Motors joined the sponsorship for the Dunlop Golf Tournament, a men’s professional competition that had been held since 1969, as the main organizer, and hosted the first Mitsubishi Galant Tournament at the Noto Country Club in 1977. This made Mitsubishi Motors Japan’s first automobile manufacturer that hosted a men’s professional golf tournament. Since its inauguration, the annual tournament gained in popularity as a circuit tournament that took players to highly challenging courses across Japan, from Hokkaido to Kyushu. Mitsubishi Motors’ products were presented as an extra prize for the winner and as a special award, which also contributed to the company’s publicity.
Starting from the 23rd competition in 1999, the tournament took on the new name “Field Mitsubishi Motors Tournament” to symbolize the support from the entire Mitsubishi Motors Group for further growth.
Mitsubishi Motors hosted the tournament until 2000 when it decide to complete overhaul of its advertising and promotional activities due to its tough financial condition at the time. The Mitsubishi Motors Group stepped down as the host in 2001, and the tournament was renamed “Mitsubishi Diamond Cup Golf” hosted by the Mitsubishi Group companies. In 2014, the tournament was renamed “Asia Pacific Open Diamond Cup Golf.”
Prev
Next
Founded Japan Automotive Engineering Co., Ltd.(currently Mitsubishi Automotive Engineering Co.,Ltd.)
Established Nagoya plant - Okazaki (currently Okazaki Plant - Okazaki).
Hosted the Mirage Bowl.
Hosted the Mirage Bowl.
As the preliminary advertising campaign for the new Mirage scheduled to be launched in March 1978, Mitsubishi Motors hosted the final game of the NCAA college football season, which enjoyed great popularity at the time, as the Mirage Bowl at Korakuen Stadium to kindle target users’ interest and enhance its public image.
The game demonstrated the authentic speed and power of a football game, along with the music played by the colleges’ marching bands and cheerleaders’ spectacular performance. The event attracted 90,000 spectators to the pre-game events and the game combined. The game that was broadcast live on TV served as the introduction of authentic football to the Japanese public.
The Mirage Bowl moved to the Japan National Stadium in 1979 and continued to enjoy a full stadium crowd every year. In 1985, after the ninth Mirage Bowl, Mitsubishi Motors decided that it had accomplished its intended goals and ceded the initiative as the host.
Prev
Next
1978
Created 2 channels of domestic distributors.
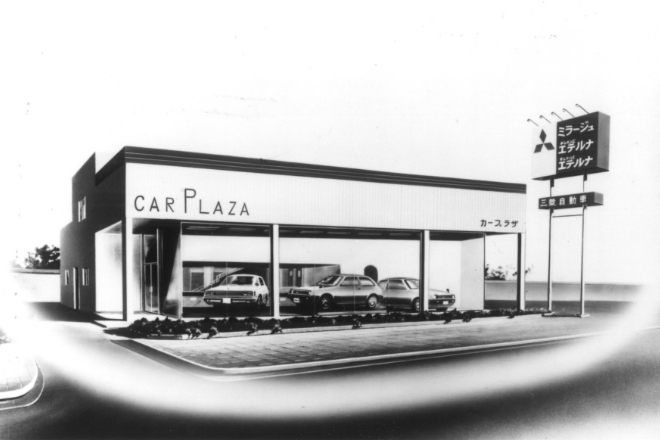
Created 2 channels of domestic distributors.
Mitsubishi Motors established Car Plaza to enhance its market (108 dealers and 186 sales offices at the time). Car Plaza dealers all opened on March 1, 1978, the day Mirage was launched. Following the establishment of Car Plaza, the company’s existing passenger car dealerships were renamed Galant Shops.
In January 2003, as part of the company’s passenger car marketing business reform in Japan, the sales systems in the two channels of Galant Shops and Car Plaza dealers were integrated into the new, full-line sales network “Mitsubishi Motors” that would deal in all lines of passenger cars. The company also gave its dealerships a makeover by adding its new corporate identity (CI) design to the interior and exterior of Mitsubishi dealers in an effort to improve customer satisfaction and its brand image. The dealers desplayed refurbished signage mostly in red and silver (the corporate colors at the time) and used simple interior designs to accentuate the beauty of the cars.
In 2016 the new brand message “Drive Your Ambition” was unveiled, and 5,000 dealers around the world took up a new design for their shops’ interior and exterior to enhance the brand image. The new design at these dealers features the basic color scheme of black, white, and gray, with dynamic red lines as accents.
Prev
Next
1979
The soccer team of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. won three titles for the first time ever.
Acquired shares in CAL of Australia.
Acquired shares in CAL of Australia.
The export of Mitsubishi vehicles to Australia began in 1957. Once it was founded, Mitsubishi Motors entered into a distributorship, trademark, and technical assistance agreement with Chrysler Australia Ltd. (CAL), which was Chrysler’s manufacturing base in Australia, as Mitsubishi and Chrysler had an equity alliance at the time. In 1971, it launched the knock-down production of the Colt Galant.
In April 1979, Mitsubishi Motors complied with a request from Chrysler to acquire shares in CAL, which had begun to scale down its international business. Mitsubishi Motors and Mitsubishi Corporation set up a joint venture to buy out CAL. In October 1980, CAL was renamed Mitsubishi Motors Australia Ltd. (MMAL; located in Adelaide). After the acquisition, Mitsubishi Motors gradually increased its ownership ratio, and eventually acquired full ownership of MMAL.
In 1985, MMAL increased the width of Galant Σ (Sigma) by 65 mm to develop a vehicle designed specifically for consumers in Australia. This product was launched as Magna with a 2.6-liter engine. MMAL also developed a station wagon based on Magna to add to the line.
In 1988, Mitsubishi Motors imported and sold the Magna station wagons at dealerships in Japan.
In 2005, MMAL developed the first new motor vehicle in nine years as Mitsubishi Motors’ manufacturer and distributor in Australia. The vehicle was a high-class sporty sedan named 380, which was launched onto the market as the last Mitsubishi vehicle manufactured in the country. Since the end of the local production in March 2008, MMAL has served as a Mitsubishi sales company to date.
Prev
Next
Established Gamagori Motor Pool in Gamagori port in Aichi Prefecture.
Launched the production of 4G6 model (Sirius Engine).
Launched the production of 4G6 model (Sirius Engine).
The 4G6 Sirius engines were developed to serve as water-cooled in-line four cylinder gasoline engines with displacement that filled the gap between the 4G3 and 4G5 engines. The 1.8 liter 4G62 model was installed in Lancer EX launched in February 1980. The 4G6 model aimed to gain internationally competitive advantages as a small, lightweight, low-cost, and high-performance engine. It was 20 kg lighter and 65 mm shorter than the 4G5 model. The 2.0 liter 4G63 model was added in April of the same year, and it became Mitsubishi Motors’ flagship passenger car engine.
This 4G6 engine was the first engine produced at the Shiga Plant that had been built in 1979.
In June 1984, the 4G63 Sirius DASH (dual action super head) engine was installed in the Galant Σ and Starion. This high-power energy-efficient engine was the first to achieve 200 horsepower for the front-wheel drive vehicles.
With the full upgrade of the Mirage and Galant for the launch in October 1987, the 1.6 liter 4G61 model was added. The Galant VR-4 launched in December of the same year was equipped with a 4G63 DOHC turbo engine with an intercooler, which delivered power as high as 205 ps/6,000 rpm. In April 1989, the 1.8 liter 4G67 model was added. In August of the same year, the 2.4 liter 4G64 model was installed in the Delica and other vehicles.
The 4G6 engine was then developed into the 1.8 liter 4D65 diesel model for passenger cars that were meant to follow the 4D5 engine. This model was installed in the Mirage and Lancer Fiore launched in December 1983. A turbocharged version of this model with an intercooler was adopted for Galant Σ in February 1984, and the 2.0 liter 4D68 model was added in May 1992.
The 4G69 model was installed in the new Grandis that was launched in March 2003. The newly developed 2.4 liter MIVEC (variable valve timing and lift mechanism) engine combined with INVECS-II4A/T delivered good engine response for smooth performance.
The production of the 4G6 Sirius engines lasted more than 30 years, which was longer than that of the 4G3 Saturn engines.
- Years manufactured: 1979–2016
- Total production: 6,360,000
- Displacement: 1,600 cc–2,400 cc
- Models equipped with these engines: Galant, Delica, Lancer EX, Mirage
Prev
Next
Established Kyoto Plant - Shiga.
1981
Offered the “silent shaft” technology to Porsche.
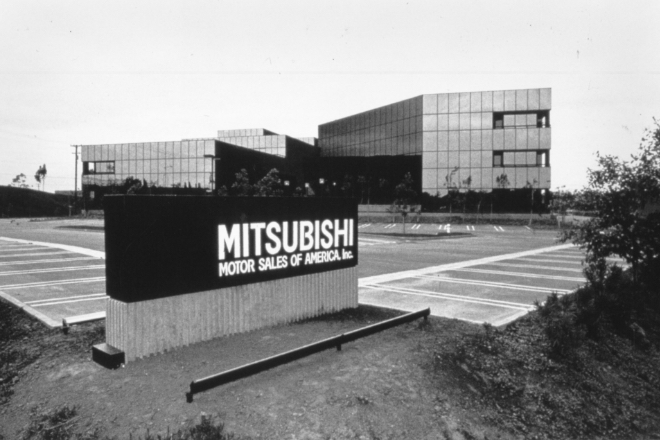
Established Mitsubishi Motor Sales of America, Inc. (MMSA) in the US.
Established Mitsubishi Motor Sales of America, Inc. (MMSA) in the US.
The export of Mitsubishi vehicles to the United States had initiated with the export of scooters in the 1950s. With the signing of the US distributorship agreement (USDA) with Chrysler in October 1970, the Dodge Colt (Colt Galant in Japan) vehicles were shipped out the same month as the first four-wheelers exported to the United States.
Chrysler had the exclusive right to distribute Mitsubishi vehicles in the United States under the USDA at the time. In 1982, Mitsubishi Motors established Mitsubishi Motor Sales of America, Inc. (MMSA; located in Fountain Valley, California) as its wholly owned distributorship. Mitsubishi Corporation also acquired shares in MMSA the following year, and then started sales of the small pickup truck Forte.
In January 2003, MMSA merged with the manufacturing company Mitsubishi Motor Manufacturing of America, Inc. (MMMA) to make a start as Mitsubishi Motors North America Inc. (MMNA; located in Cypress, California) to manage sales, production, finance, and R&D in North America.
MMNA discontinued its manufacturing business in November 2015. It has served as a Mitsubishi vehicle sales company in the United States to date.
Prev
Next
1982
Introduced the variable displacement engine “MD”.
Introduced the variable displacement engine “MD”.
Modulated displacement (MD) is an engine technology that allows the vehicle to automatically run on two or four cylinders according to how it is driven. The engine basically is a 1.4-liter four-cylinder engine, but uses computer control to close the intake and exhaust valves for two cylinders, so that the vehicle runs on two cylinders when it sits idle, decelerates, runs at a constant speed of up to around 70 km per hour (in 4th gear), or in other low-load condition. During acceleration and high-speed driving and other high-load conditions, it runs on four cylinders. This MD technology dramatically improved fuel efficiency (20 km per liter in its 10 mode).
This MD engine, which is a type of cylinder deactivation engine, was installed in the Mirage in the same month.
Prev
Next
Began using the MMC symbol for the front emblem.
Acquired shares in Hyundai Motor Company of South Korea.
1983
Established PROTON in Malaysia.
Established PROTON in Malaysia.
Perusahaan Otomobil Nasional Sdn. Bhd. (PROTON; located in Shah Alam, Malaysia) was founded as a joint venture by Mitsubishi Motors, Mitsubishi Corporation, and Heavy Industries Corporation of Malaysia Bhd. (HICOM), under then-Malaysian Prime Minister Mahathir Mohamad, who envisioned establishing a national car company.
With support provided by Mitsubishi Motors and Mitsubishi Corporation, the production of Saga as Malaysia’s first national car, which was based on Mitsubishi Motors’ Lancer Fiore, began in 1985. In 2000, PROTON launched Waja, its first independently developed vehicle. In February 2004, the company launched GEN-2 equipped with its independently developed engine, demonstrating its technological competence that only became greater each year and gaining public support as the symbol of Malaysia’s industrialization.
As PROTON reached an advanced technical level, Mitsubishi Motors sold all shares it held in the Malaysian company to terminate the equity alliance in 2004.
In March 2005, Mitsubishi Corporation and Edaran Otomobil Nasional Berhad (ECO), which was a PROTON dealer, jointly established Mitsubishi Motors Malaysia Sdh. Bhd. (MMM), and Mitsubishi Motors entered into a distributorship and service agreement with MMM the following month. Mitsubishi vehicles are sold in the Malaysian market via MMM.
The cooperative ties between Mitsubishi Motors and PROTON continued after the termination of the equity alliance, through licensing of technologies for components as well as engine and transmission trading. In February 2006, the two companies signed a memorandum for a new alliance to collaborate in development and production. In December 2008, Mitsubishi Motors entered into an agreement with PROTON for development and production of a new motor vehicle.
Prev
Next
1984
Established Ralliart, Inc.
Established Ralliart, Inc.
As motorsport enjoyed a growing number of fans, Ralliart, Inc. was established to meet the diversified needs of car users and foster sound awareness of motorsport. Its objectives were to provide a range of excellent services for motorsport lovers in Japan and overseas, develop motorsport parts and gear, and establish a solid distribution system for those products.
The major part of Ralliart’s business consisted of the activities shown below. In addition to the motorsport business, the company ran side projects to raise awareness of road traffic safety, such as organizing driving lessons for women.
(1) Getting involved in various motorsport events in Japan and overseas
(2) Planning and managing a range of services for motorsport fans, training sessions for people who sought to obtain a license, and auto racing workshops
(3) Developing and marketing motorsport parts and gear
(4) Developing and marketing a range of character (Ralliart) goods
Since its establishment, Ralliart had the privilege of enjoying support from numerous customers while it engaged in activities for motorsport. However, Ralliart scaled down its operations at the end of March 2010 after Mitsubishi Motors announced its team’s hiatus from the WRC (FIA World Rally Championship) in December 2005, and the discontinuation of its team’s activities in the Dakar Rally in February 2009. With the downsizing, Ralliart discontinued the operation and management of the overall activities for user support in motorsport excluding the sales of Ralliart goods.
Prev
Next
Integrated Mitsubishi Motor Sales Company.
Integrated Mitsubishi Motor Sales Company.
With the domestic and international business environment growing tougher owing to the second oil crisis in 1979, Mitsubishi Motors and Mitsubishi Motor Sales Company (“Mitsubishi Motor Sales”) entered into a business transfer agreement on May 28, 1984, as a step toward integration. The agreement was to enable the two companies to quickly respond to changes in the business environment surrounding Mitsubishi Motors and to user trends, and to pursue development and marketing based on accurate knowledge of market needs. This integration did not take the form of a merger. Instead, Mitsubishi Motor Sales transferred its business in Japan to Mitsubishi Motors. Following this business transfer, all employees of Mitsubishi Motor Sales who were on the payroll on the transfer date also became Mitsubishi Motors employees.
The integration of Mitsubishi Motors and Mitsubishi Motor Sales marked the end of the history of separation between engineering and marketing at Mitsubishi Motors, which had continued since the establishment of Fuso Motors Sales Co., Ltd. in December 1949.
Prev
Next
1985
Electronically Controlled Suspension (ECS) won the Technological Development Award of the Society of Automotive Engineers of Japan, Inc.
Electronically Controlled Suspension (ECS) won the Technological Development Award of the Society of Automotive Engineers of Japan, Inc.
Electronic control suspension (ECS) was designed to automatically control a vehicle’s suspension characteristics (the spring constant and shock absorbers’ damping force) to keep them in the optimum state in changing driving conditions, thereby delivering a comfortable ride and controllability. ECS also had the function of keeping stable the vehicle height, in order to adjust to changes in the weight of loads/passengers, speed, and road conditions, along with the extra high ride height function that increased the ride height by 40 mm while the vehicle was parked.
Prev
Next
Established the brand message: Ii-machi, Ii-hito, Ii-kuruma (“Great Town, Great People, Great Cars”)
Established DSM (later Mitsubishi Motor Manufacturing of America Inc., or MMMA) in the US.
Established DSM (later Mitsubishi Motor Manufacturing of America Inc., or MMMA) in the US.
In 1981, voluntary export restraints were imposed on the export of automobiles to the United States. While the restraints continued, Mitsubishi Motors decided to launch local production. In 1985, the company established Diamond Star Motors Corporation (DSM; located in Normal, Illinois) jointly with Chrysler, with which it had an equity alliance at the time.
In 1988, a new plant was built in Illinois to launch the production of the Eclipse and In1990, they were imported to be sold via sales companies in Japan.
In October 1991, Mitsubishi Motors bought all shares Chrysler held in DSM and, in July 1995, it changed the name of DSM to Mitsubishi Motor Manufacturing of America, Inc. (MMMA; located in Normal, Illinois).
In January 2003, MMMA merged with the local sales company Mitsubishi Motor Sales of America, Inc. (MMSA) to make a start as Mitsubishi Motors North America Inc. (MMNA; located in Cypress, California) to manage sales, production, finance, and R&D in North America.
Production by MMNA surpassed 220,000 in 2000. However, in the wake of the termination of manufacturing as an OEM for Chrysler and the collapse of Lehman Brothers, production dipped dramatically to 20,000 in 2009.
MMNA began the production of the Outlander Sport (RVR in Japan) in 2012 to improve production efficiency and raise the production and capacity utilization rate, which was geared toward not only the North American markets, but Russia, the Middle East, and Latin America.
However, exports to Russia, which had made up 30 percent of the company’s production, dropped dramatically in late 2014. The manufacturing of vehicles by MMNA had to be transferred to the Okazaki Plant because of this significant decrease, and at the end of November 2015, the manufacturing business in the United States was discontinued.
Prev
Next
Launched the production of 6G7 model engine.
Launched the production of 6G7 model engine.
The 6G7 engines were the first V-type six-cylinder gasoline engines developed for Mitsubishi Motors’ passenger cars. The 2.0 liter 6G71 and 3.0 liter 6G72 models were installed in the fully restyled Debonair V in August 1986.
In May 1990, the 2.5 liter 6G73 model installed in Diamante served as a pioneer of the 2.5 liter engine market.
In October 1992, the 3.5 liter 6G74 model was installed in Debonair, and later in Pajero.
The 3.8 liter 6G75 model was installed in Endeavor, the SUV launched exclusively onto the North American market in 2003. In Japan, it was installed in Super Exceed, the highest-grade Pajero, in November 2005. The engine was designed to deliver a quieter and smoother ride with a premium feel. Although its maximum power of 219 ps and maximum torque of 34.3 kg-m were almost the same as the conventional 6G74 model, they met the 2005 exhaust emission standards.
- Years manufactured: 1985 - present
- Total production: 8,080,000 (at the end of 2018)
- Displacement: 2,000 cc - 3,800 cc
- Models equipped with these engines: Debonair V, Pajero, Diamante, Debonair
Prev
Next
1986
Acquired shares in CMC of Taiwan.
1987
Established PAMCOR (currently MMPC) in the Philippines.
Electronically controlled power steering “EPS” won the Technological Development Award of the Society of Automotive Engineers of Japan, Inc.
Electronically controlled power steering “EPS” won the Technological Development Award of the Society of Automotive Engineers of Japan, Inc.
Electronic Power Steering (EPS) achieved a much-awaited significantly lighter feel to maneuvers for parking than conventional power steering. Its straight-running stability delivered a smooth ride at low speed, and an optimal and improved steering feel for a ride at high and medium speed.
EPS was adopted for Galant Σ and Eterna Σ that were launched in 1983.
Prev
Next
Established Suiryo Service Co., Ltd.
Introduced active electronically controlled suspension, “Active ECS”.
Introduced active electronically controlled suspension, “Active ECS”.
Active ECS (Active Electronic Control Suspension) electronically controls the internal pressure of the shock absorbers and air springs installed in the front and rear suspensions independently on all four wheels, enabling the vehicle to maintain its body posture nearly parallel to the road surface even when driving conditions change due to road surface conditions.
This Active ECS is designed to control the inner pressure of the air springs, in addition to ECS’s functions to switch between running soft and hard and to control the car height that were already used for Mitsubishi vehicles on the market. Controlling the inner pressure minimizes car body roll during cornering; the lift/dip of the front/rear of the car when the vehicle is started, accelerated, or brake; and bouncing up and down when the vehicle runs over bumps. This was developed as the world’s first active control on the leveling of chassis height added to the ECS technology, delivering smooth handling, and a comfortable steady ride, coupled with greater starting ability and braking stability. Active ECS was used for the Galant that was launched the same year.
In 1988, this technology won the Technological Development Award of the Society of Automotive Engineers of Japan, Inc.
Prev
Next
Mizushima plant achieved production of a cumulative total of 10 million units.
1988
Established property management companies at each plamts.
Established Mitsubishi Auto Credit-Lease Corporation.
Offered the “silent shaft” technology to Volvo.
Shares listed on First Section of stock exchanges.
1989
Established Mitsubishi Motors Europe B.V. (MME) in the Netherlands.
Established Mitsubishi Motors Europe B.V. (MME) in the Netherlands.
The export of Mitsubishi vehicles to Europe began in 1956. In 1971, the year Mitsubishi Motors was established, Chrysler had the exclusive right to distribute Mitsubishi vehicles in Europe under the distributorship agreement signed between the two companies in an equity alliance.
In 1974, Chrysler agreed that Mitsubishi Motors would launch business activities on its own in the region. In August of the same year, Mitsubishi Motors became the first Japanese automobile distributor in Europe when it entered into a full-line dealership agreement with a local enterprise to sell its vehicles in Belgium and Luxembourg. Following the agreement, the company started sales of Galant and Lancer.
In 1977, Mitsubishi Motors opened Liaison Office Europe (LOE; located in Rotterdam, the Netherlands) or “Europe Office” as known in Japan, as its representative office for information gathering and research. The company also established MMC Truck Parts Europe B.V. (MTP; located in an eastern suburb of Schiphol, the Netherlands) as a component storage depot it wholly owned to ensure the supply of spare parts for Mitsubishi vehicles exported to Europe. In January 1989, MTP was renamed Mitsubishi Motors Europe B.V. (MME; located in Amsterdam, the Netherlands).
In April of the same year, MME took on the responsibility to oversee Mitsubishi Motors’ overall business in Europe, including business operation needed to be a certified enterprise, technical studies and research.
In April 1993, Mitsubishi Motors established Mitsubishi Motors R&D Europe GmbH (MRDE in Trebur, Germany) responsible for design, tests, and authorization to further enhance its marketing and distribution in Europe, and Mitsubishi Motors Sales Europe B.V. (MMSE in Amsterdam, the Netherlands) for marketing and selling vehicles and components in close conjunction with distributors across Europe, along with a range of services.
In December 2002, MMSE, as a full-line sales company, was integrated into MME to form the business that oversees Mitsubishi Motors’ business in Europe. The objective of this integration was to ensure greater consistency in the business in this region that encompasses the sales and marketing of products, parts, and goods, as well as the supervision of distribution and the production business.
Today, MME oversees Mitsubishi Motors’ business in Europe, and MRDE conducts motor vehicle-related research, tests, and studies.
Prev
Next
Offered the “silent shaft” technology to SAAB.
Introduced a flexible hours schedule called “flex time”.
Conducted the first ever capital increase through public stock offering since being listed.
Conducted the first ever capital increase through public stock offering since being listed.
In December 1988, Mitsubishi Motors listed its stock shares on the first sections of the Tokyo, Osaka, and Nagoya Stock Exchanges. One year later, the company conducted its first public offering to raise additional capital (1,110 yen per share, 80 million shares in total). Out of the total of 88.8 billion yen that was raised, 44.4 billion yen was capitalized. The company’s capital after this public offering added up to 109.47745 billion yen (853.89 million shares issued in total).
▶ Click here to visit the corporate profile page
Prev
Next
1990
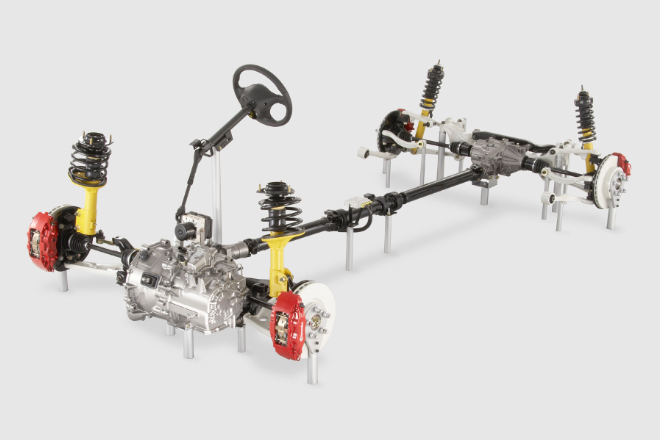
Introduced traction control system “TCL”.
Introduced traction control system “TCL”.
The Traction Control System (TCL) is designed to prevent the vehicle from skidding out of the lane due to excessive acceleration when cornering. The TCL is an ideal driving force control device equipped with the trace control and slip control functions. The trace control function, the world’s first technology, makes full use of a computer to detect how the car is driven based on the speed and steering angles, so that the engine output is automatically and optimally controlled to prevent excessive lateral acceleration. The slip control function is to avert the vehicle from slipping when it is started and accelerated on a slippery road surface, such as a snow-covered road.
In 1991, this technology won the Technological Development Award of the Society of Automotive Engineers of Japan, Inc.
Prev
Next
Introduced Mitsubishi intelligent cockpit system “MICS”.
Introduced Mitsubishi intelligent cockpit system “MICS”.
The Mitsubishi Intelligent Cockpit System (MICS) is designed to adjust the positions and angles of the seat, rearview mirror, side view mirror, and steering wheel all at once. It also has the functions to identify people, deduce the position suitable for each physique based on ergonomics data, and judge conditions for easy getting in and out of the car, so that adjustments are quickly made to keep the driver’s seat and the space around it easy-to-use. These functions make it easy for drivers to obtain a safe and comfortable driving environment.
Prev
Next
The soccer team of Mitsubishi Motors Corporation (later Urawa Red Diamonds) launched its activities.
Changed the name of Shinryo Automotive Service Co., Ltd. to Mitsubishi Automotive Techno-Service Co., Ltd.
1991
Launched the production of 4G9 model engine.
Launched the production of 4G9 model engine.
The 4G9 engines were developed as a new line of in-line four cylinder gasoline engines. They were the products of the thorough pursuit of highly efficient, small and lightweight engines. In June 1991, the 1.8 liter 4G93 model was installed in RVR. Following this, the new Mirage and Lancer launched in October of the same year were equipped with the 1.5 liter 4G91 model and the 1.6 liter 4G92 model.
In October 1992, the Mitsubishi Innovative Valve Timing and Electronic Control system (MIVEC) was built in the Mirage and Lancer. MIVEC was a 4G92 DOHC that delivered the high performance of 110 ps and the fuel efficiency of 16.0 km per liter in the 10-15 mode.
In October 1993, the MVV system was adopted for the 4G93 SOHC to be installed in the Galant and Eterna.
The 2.0 liter 4G94 GDI engine was installed in Pajero iO that was launched in June 2000. Acceleration performance was improved, and in 2010, it met the new fuel efficiency standards (2WD vehicles with three doors excluded) and conformed to the 2000 vehicle emission control requirements (applied to all vehicles).
- Years manufactured: 1991–2014
- Total production: 2,450,000
- Displacement: 1,500 cc–2,000 cc
- Models equipped with these engines: Lancer, Mirage, Galant, Pajero iO, Lancer Cedia
Prev
Next
Introduced the Caregiver Leave System.
Launched the production of 6A1 model engine.
Launched the production of 6A1 model engine.
6A1 series engine series was developed as the successor to the 6G7 series V6 engines. The 1.6 liter 6A10 model was the world’s smallest V6 engine installed in the Mirage that was launched in January 1992. 1.8 liter 6A11 and 2.0 liter 6A12 were installed on Galant and Eterna that were launched in May 1992. What is notable about the 6A12 model is that it was the first engine of this class that used a twin-turbocharger and an intercooler.
The Galant and Legnum that were launched in August 1996 adopted the 6A13 model, which used a 2.5 liter V6 DOHC twin-turbo intercooler with the maximum output of 280 ps and the maximum torque of 37.0 kg-m. This engine was installed in VR-4 and delivered a powerful ride, with its highest-level power in the class, delivered a powerful ride.
- Years manufactured: 1991–2007
- Total production: 320,000
- Displacement: 1,600 cc–2,500 cc
- Models equipped with these engines: Lancer, Mirage, Galant, Diamante
Prev
Next
Issued unsecured bonds with warrants.
Changed the name of Daiya Automotive Transportation Co., Ltd. to Mitsubishi Automotive Logistics Co., Ltd.
Hosted Star Camp.
Hosted Star Camp.
Mitsubishi Motors hosted the Star Camp across Japan, with the support of the local government of the venue. The objective of the event was to promote activities in close contact with nature through car camping so that participants would learn the importance of the natural environment. As one of the country’s biggest camping events, the Star Camp enjoyed 1,000 groups of participants every year from 1991 to 1997.
In 2007, it was held for the first time in ten years and continued until 2015 as an annual event in Asagiri Kogen, Shizuoka, for fans of automobile tourism and camping across Japan.
Since 2017, the Star Camp has been held in more than one venue, offering activities designed for a wide range of participants to enjoy the outdoors. These activities include family programs designed so that for both adults and small children can enjoy and programs to provide hands-on lessons to acquire know-how that can be useful outdoors. There were also test drives to experience the performance of a Mitsubishi sports utility vehicle (SUV) or 4WD, and a movie played using electricity stored in the vehicle provided by the power supply function of Outlander PHEV.
Prev
Next
Introduced vertical vortex lean-burn engine, “MVV”.
Introduced vertical vortex lean-burn engine, “MVV”.
The Mitsubishi Vertical Vortex (MVV) engine was released featuring the formation of two large vertical vortices, an "air-only vertical vortex" and a "mixture (air and gasoline) vertical vortex," in the intake air flow drawn into the cylinder through the ingenious shape of the intake port and other means. The movements of these vortexes coupled with the design of the most suitably shaped combustion chamber enables stable combustion even when the mixture inside the cylinders is extremely lean, with the air-fuel ratio of up to around 1:25, far exceeding the theoretical air fuel ratio which is about 1:14.7 in the case of gasoline.
It is difficult to stabilize combustion if the air is leaner than the theoretical air-fuel ratio. Hence, Mitsubishi Motors worked on research and development in multiple fields and, consequently, created the engine with cleaner emissions that made driving easier and improved fuel efficiency by applying the world’s first vertical vortex technology.
Mitsubishi Motors also adopted the all-range air fuel ratio sensor designed to measure the air-fuel ratio in all operating ranges. With this sensor, the engine’s fuel efficiency was up a little more than 20 percent (in the 10 mode), while the output and ease of driving were almost the same as conventional engines.
In 1992, this technology won the Technological Development Award of the Society of Automotive Engineers of Japan, Inc.
Prev
Next
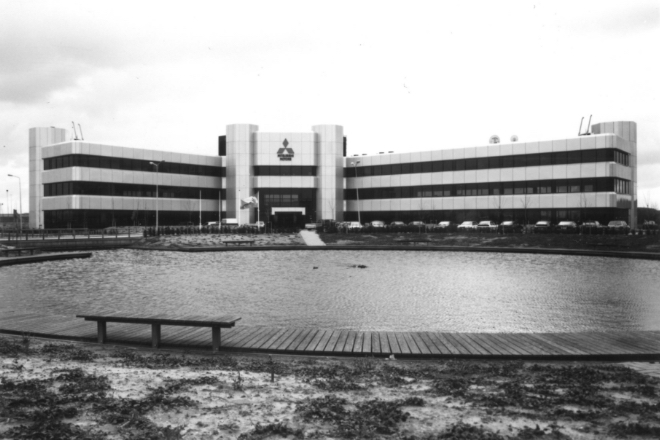
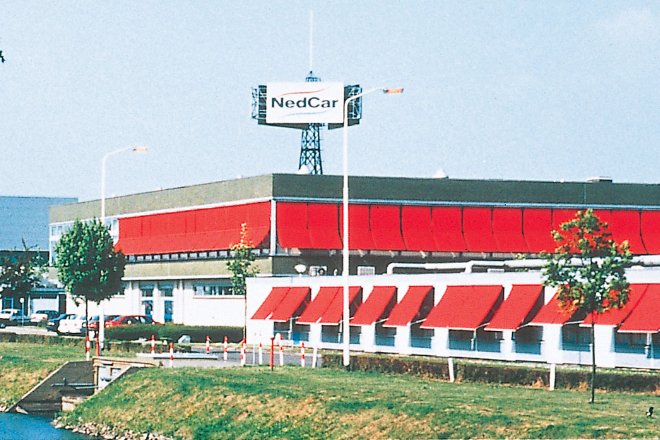
Established Netherlands Car in the Netherlands.
Established Netherlands Car in the Netherlands.
In August 1991, Mitsubishi Motors acquired shares in Volvo Car B.V., a joint venture established to manufacture passenger cars in the Netherlands under the agreement for a joint passenger car business signed between the Dutch government and Volvo.
In December of the same year, the business was renamed Netherlands Car B.V. (NedCar; located in Limburg, the Netherlands). Mitsubishi Motors became the first Japanese automobile manufacturer that launched local production in the heart of Europe.
In May 1995, NedCar began the production of the five-door hatchback Carisma, which Mitsubishi Motors had developed for the European market. In October the following year, four-door Carisma sedans (with a right-hand steering wheel) made by NedCar were exported to Japan for sale.
After the Dutch government withdrew from this joint venture in 1999, and Volvo in 2001, NedCar became Mitsubishi Motor’s wholly owned subsidiary.
However, Mitsubishi Motors reviewed its production network around the world in the context of the dramatically changing environment surrounding the automotive business. As a result of this review, the company entered into a master agreement with VDL Groep B.V. (VDL; located in Eindhoven, the Netherlands) for the transfer of all shares it held in NedCar on July 11, 2012. On December 14, Mitsubishi Motors completed the transfer to VD Leegte Beheer B.V. (VDL’s wholly owned subsidiary), which marked the end of its vehicle manufacturing at NedCar as its production base in Europe.
Prev
Next
1992
Introduced Senior Reemployment System (Senior System).
Introduced active safety system “INVECS”.
Introduced active safety system “INVECS”.
The Intelligent & Innovative Vehicle Electronic Control System (INVECS) was the world’s first technology designed to recognize and judge changes in where the vehicle ran on behalf of the driver and rightly control the car as the driver would intend to (fuzzy control). The system consists of six functions, namely the fuzzy shift 4AT, fuzzy TCL, electronically controlled full-time 4WD, active 4WS, active preview ECS, and air purifier for fuzzy air conditioning. In 1993, this technology won the Technological Development Award of the Society of Automotive Engineers of Japan, Inc.
1. Fuzzy shift 4AT
This function is to recognize the degree of each slope/curve to control the engine output.
2. Fuzzy TCL
In addition to the conventional TCL (Traction Control System), a function that recognizes flat roads, uphill and downhill, and controls and regulates engine output.
3. Electronically controlled full-time 4WD
This full-time 4WD electronically controls the distribution of driving force applied to the four wheels in line with the road and driving conditions. The ratio of driving force distributed to the front and rear wheels is basically 32:68, and to the rear wheels and right/left wheels 50:50. This was also the world’s first technology that combined 4WD and TCL.
4. Active 4WD
The front and rear wheels are steered into the same direction (coordinated control) to keep the vehicle body level over the road when the car switches lanes at high speed. This function is to automatically adjust instantaneous reversed control in the low- to mid-speed range and the rear wheel steering angle in line with the road condition, to this conventional coordinated control to keep the vehicle even more stable.
5. Active preview RCS
In addition to the conventional active electronically controlled suspension "Active ECS," the system detects the road surface conditions in front of the vehicle using ultrasonic waves and recognizes road gradients to control vehicle stability.
6. Air purifier for fuzzy air conditioning
This function is to apply fuzzy control to the overall temperature and humidity using an air purifier.
Prev
Next
Introduced variable valve timing engine “MIVEC”.
Introduced variable valve timing engine “MIVEC”.
The Mitsubishi Innovative Valve Timing and Lift Electronic Control System (MIVEC) is an engine equipped with the variable valve timing and displacement technology. It is designed to automatically switch between its three modes according to where and how the vehicle runs. These modes are the high-speed mode when the car is going fast; the low-speed mode when the car starts, acclerates, and/or ascends a slope; and the MD (variable displacement) mode when it runs in an urban area. The innovative variable valve timing technology delivers high output, low fuel consumption, and clean performance, thereby enabling highly efficient driving ideal for drivers. MIVEC was first used for the Mirage in 1992. Improvements were continuously made to it thereafter for greater performance. A mechanism that continuously optimally controls intake and exhaust valve timing was adopted in the Outlander launched in 2005, the Delica D:5 launched in 2007, and the Galant Fortis. This system, which constantly varied the cams on the intake side and exhaust side separately, enables more precise control based on the engine speed and load than a system designed to control only the intake side, achieving high output, low fuel consumption, and clean performance at a high level.
The new MIVEC engine is designed for constant variable control of intake valve timing and valve lift volume with its simply structured SOHC. It was adopted for the RVR, Galant Fortis, Galant Fortis Sportback, and Delica D:5 that were launched in 2011, and for the Outlander launched in 2012.
Prev
Next
Launched the production of 4M4 model diesel engine.
Launched the production of 4M4 model diesel engine.
The 4M4 series engine series was developed to achieve both high output and low emissions for passenger car diesel engines. In July 1993, the 2.8 liter 4M40 turbo engine with an intercooler was installed in the Pajero. This engine made the vehicle considerably easier to drive, achieving the greatest torque in this class (30 kg-m/rpm). In 1992, it met the diesel vehicle emission control requirements. Moreover, various measures were taken to reduce vibrations and noise.
In September 1999, the Pajero was fully restyled for the first time in eight and a half years. It was equipped with the 3.2 liter 4M41, which is an in-line 4-cylinder diesel engine with 4-valves per cylinder, a DOHC valvetrain, and intercooler-turbocharger. This newly developed engine of the new generation was an evolved diesel engine designed to achieve high output, high torque, and low fuel consumption. It boasted the output of up to 175 ps and the torque of up to 39 kg-m/rpm, which were the highest power in the class and increased fuel efficiency by 27 percent compared to conventional engines. In 2005, it met the fuel efficiency standards for diesel vehicles. With the adoption of new technologies for injection pumps, catalyst, the engine also met long-term emission control requirements.
- Years manufactured: 1992–2018
- Total production: 1,010,000
- Displacement: 2,800 cc–3,200 cc
- Models equipped with these engines: Pajero, Mitsubishi Jeep
Prev
Next
1993
Established the brand message: Creating Together.
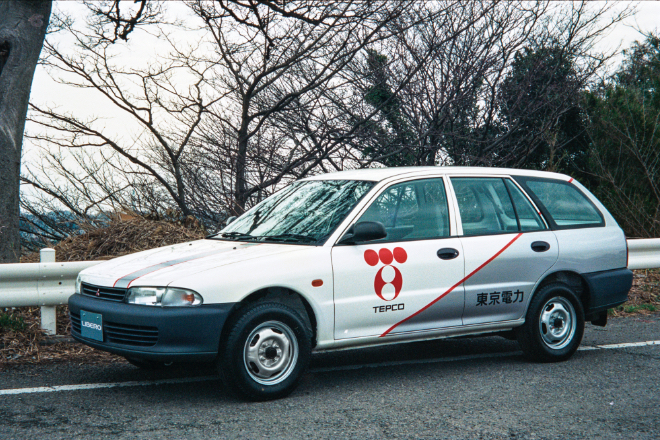
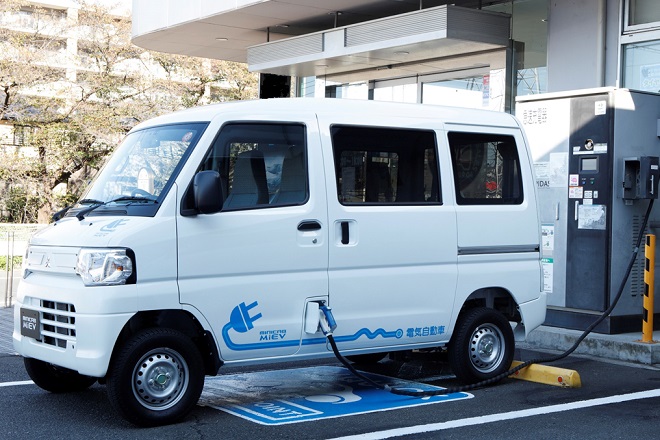
Developed Libero electric vehicle in collaboration with Tokyo Electric Power Company.
Developed Libero electric vehicle in collaboration with Tokyo Electric Power Company.
Mitsubishi Motors developed the Libero electric vehicle (Libero EV) in collaboration with Tokyo Electric Power Company, and sold 36 to government agencies and major corporations.
Libero EV was developed by replacing parts of Libero Cargo with those of electric vehicles. Based on the results of an assessment of Lancer Van EV, Libero EV was equipped with lead batteries, a motor, and a transmission designed specifically for the vehicle. In addition, it had greater suspension and braking, low rolling resistance tires, an electric heat pump for air conditioning, electric power assisted steering, and other technologies for high efficiency, thereby achieving the mileage of 165 km with a single charge (at the constant speed of 40 km per hour) and the acceleration performance of 4.1 seconds for 0-40 km per hour (maximum speed of 130 km per hour). The manufacturer's suggested retail price was 11.23 million yen.
Prev
Next
Established Mitsubishi Motor Sales Europe B.V. (MMSE) in the Netherlands.
Set up Automobile Information Service for Children.
Set up Automobile Information Service for Children.
In 1992, the social studies textbook for fifth graders highlighted that the automotive industry was Japan’s iconic key industry, in place of the steel industry that had always been listed as one. Following this, information requests from elementary school teachers and children were in surge, as did requests for our corporate profile and a wide range of queries and consultations.
In response to this growing interest, Mitsubishi Motors made internal arrangements to open an Automobile Information Service for Children to answer more questions actively and meet their requests.
Mitsubishi Motors was the only company in the automotive industry that launched this unique initiative of offering information services for school children. It runs from late July to early December each year to receive and answer a variety of questions about the automotive industry in general by phone (toll-free) and by mail. We have also offered an email information services for elementary school children since 2009.
Web page designed as a learning tool for children is always available, which illustrates the process from product development to sales and presents animations and videos showing how cars are produced at a plant. Furthermore, the free pamphlet “Why, Why, Car Making Research Kids” is available from the Automobile Information Service for Children. It illustrates in simple terms what process a car goes through before it is complete, what a manufacturing plant looks like, how an electric vehicle works, and what initiatives Mitsubishi Motors take for the environment and automotive safety, among others, using photos and pictures.
Prev
Next
1994
Achieved post-war production of a cumulative total of 25 million units of four-wheeled vehicles.
Achieved production of a cumulative total of 25 million engines.
Published an environmental brochure titled Soshite Ashita E (“Toward the Future”).
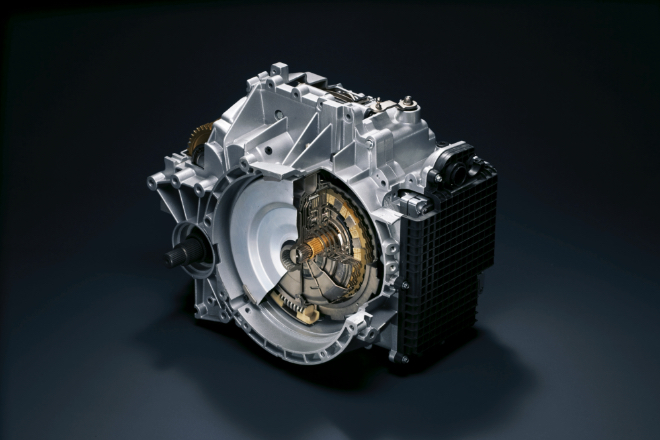
Introduced automatic transmission “INVECS-II”.
Introduced automatic transmission “INVECS-II”.
Intelligent & Innovation Vehicle Electronic Control System-II (INVECS-II) evolved from the INVECS that was developed in 1992. It had the function of learning the driver’s tendencies and preferences so that it would change gear at the best timing the best timing for the driver. Its computer also had the latest logic circuit for optimum control to select the gear suited to the driving condition with high precision. With its automatic gear shifting, INVECS-II is the transmission that delivers a safe and comfortable ride in driving gear, regardless of the driving condition.
In addition, an epoch-making AT with a "sport mode" function, which allows the driver to enjoy sports driving as if shifting gears manually, was also developed.
In 1995, this technology won the Technological Development Award of the Society of Automotive Engineers of Japan, Inc.
Prev
Next
1995
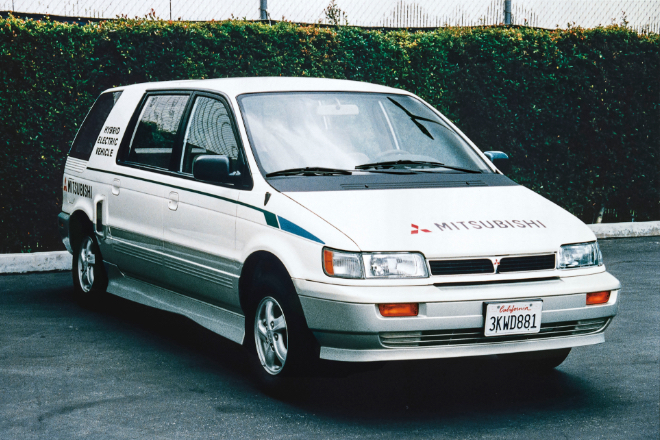
Manufactured a prototype of hybrid electric vehicle, and conducted tests in collaboration with California Air Resources Board.
Manufactured a prototype of hybrid electric vehicle, and conducted tests in collaboration with California Air Resources Board.
As a hybrid electric vehicle that combined electric cars’ clean emissions and gasoline cars’ maneuverability, Mitsubishi Motors developed the Mitsubishi Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV) equipped with an engine for generating and charging electricity that ran on a motor. In April of the year, Mitsubishi Motors became the world’s first automobile manufacturer that entered into an agreement for vehicle tests with the California Air Resources Board (CARB) in the United States and tested three Mitsubishi HEVs to see if they were suited for practical use.
The key features of this newly developed HEV were:
1. The vehicle mostly ran on a motor and batteries (“battery-driven”), achieving zero exhaust emissions.
2. The small power generator using a gasoline engine automatically starts to generate electricity as energy stored in the batteries drops to a certain level (50 percent or less). Then the vehicle switches to the hybrid power mode to charge the batteries. Once the batteries are charged, it automatically switches back into the battery-driven mode. By repeating this process, HEV achieved the cruising distance that was impossible for EVs that ran on batteries alone.
3. The vehicle’s driving force is generated solely by the motor and its electricity is generated in the cleanest state of a gasoline engine.
4. The engine automatically engine stalls when the vehicle waits at a traffic light or gets stuck in a traffic jam without the driver turning the engine off, achieving zero exhaust emissions.
5. The motor switches into the power generator mode as soon as the driver takes his/her feet off the gas pedal or steps on the brake, thereby converting the generated kinetic energy into electric energy to be stored in the batteries.
Prev
Next
Introduced cylinder gasoline direct injection engine (GDI).
Introduced cylinder gasoline direct injection engine (GDI).
The cylinder gasoline direct injection (GDI) engine injects gasoline directly into the cylinders just as a diesel engine does, thereby enabling high-precision fuel control as well as leaner and highly efficient combustion.
Conventional gasoline engines have only limited control of fuel supply and combustion because gasoline must be mixed with air through the intake port before it is supplied to the cylinders. The GDI engine, on the other hand, is an ultimate high-efficiency engine that boasts far lower fuel consumption than diesel engines, along with higher output than conventional gasoline engines. Mitsubishi Motors was the first in the world to successfully develop and put this type of engine into practical use.
The main structure of the GDI engine consists of Upright intake boats, curved- top pistons, high-pressure fuel pump, and high-pressure swirl injectors, among others.
In 1997, this technology won the Technological Development Award of the Society of Automotive Engineers of Japan, Inc.
Prev
Next
All four of the company’s teams entered the 22nd Japan Amateur Baseball Championship, Kawasaki Baseball Team won the title for the first time, and Kyoto Baseball Team came second.
Developed an advanced safety vehicle “Mitsubishi ASV”.
Developed an advanced safety vehicle “Mitsubishi ASV”.
The Ministry of Transport (the present Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism) proposed the Advanced Safety Vehicle (ASV) Project and set up the Study Group for Promotion of ASV to pursue the plan. As part of the Study Group’s activities, Mitsubishi Motors completed Mitsubishi ASV that incorporated the most advanced safety technologies for research purposes.
The company had worked on research and development for ASVs for several years considering car safety technologies for drivers, vehicles, traffic environments, and all other aspects of the use of automobiles.
Mitsubishi ASV was developed to provide safety in two areas to clarify the research subject.
One was an “ASV for accident prevention” based on the concept of active safety, which was to have the vehicle predict and control road and driving conditions in place of the driver wherever possible, ensuring that any driver would enjoy the safety and comfort offered by the excellent performance of the vehicle. The concept was developed into the co-driver system designed to take the driver’s place when he/she was being careless (the cause of most accidents). The computer in this system alerted the driver to any danger and, in an emergency, maneuvered the vehicle to avert the danger in place of the driver.
The other was an “ASV for collision protection” to protect the driver and passenger as well as pedestrians in case of an accident. This ASV had a strong cabin structure that was optimized by the application of new materials and it was equipped with more than one airbag to protect the driver and passenger from the impact of various collisions, thereby providing extra safety in any collision.
Furthermore, other detailed features were added to the vehicle for safety of the pedestrian including a car hood developed to absorb collision energy in order to reduce damage to the person’s head when it hits the hood.
Mitsubishi Motors’ leading-edge computer simulation technology was used to develop these features of an ASV for collision protection.
Prev
Next
1996
Established MRDA in the US.
Established MRDA in the US.
Mitsubishi Motors established Mitsubishi Motors R&D of America, Inc. (MRDA; located in Bloomington, Illinois) in 1996 as its research and development business in the United States and started its business on April 1 the same year.
In the US market at the time, the Big Three--General Motors, Ford, and Chrysler--aggressively developed and launched new vehicles. With Japanese automobile manufacturers also increasing their local production, market competition grew intense over the years. The idea behind the establishment of MRDA was that to fortify the automobile business, it was essential for Mitsubishi Motors to gain greater competitive advantages by enhancing its products through research and development. MRDA enabled us to be aware of the market needs going forward and actively pursue designs that would greatly appeal to customers’ personal preferences and provide support in local purchasing. Furthermore, by having MRDA work in closer conjunction with Mitsubishi Motor Manufacturing of America, Inc. (MMMA) and Mitsubishi Motor Sales of America, Inc. (MMSA) for mutual support, our business in the US market grew stronger.
Cuurently, MRDA is responsible for research, tests, and studies in the United States.
Prev
Next
Established Tama Design Center.
Introduced active yaw control system “AYC”.
Introduced active yaw control system “AYC”.
The Active Yaw Control system (AYC) is a pioneering system designed to achieve dramatically greater motor vehicle safety. It has a function to create the yaw moment for the vehicle using the difference in driving force between the right and left tires. The yaw moment applied to the rear tires of a 4WD vehicle reduces the load on the front tires during cornering.
The AYC and ASC are systems developed as contributions to the enhancement of motor vehicles’ basic performance, namely running, cornering, and stopping to meet the demand of the times for greater car safety. When combined, these systems work for each other to make the vehicle “fun to drive” and achieve much greater safety.
Prev
Next
Introduced active stability control system “ASC”.
Introduced active stability control system “ASC”.
The Active Stability Control system (ASC) is designed to stabilize the vehicle. It adds brake pressure and yaw rates (automatic speed of the car body) to the sensor and, when its computer judges that the vehicle’s movement is about to exceed the limit of the car’s cornering performance, the brake for the four wheels is independently controlled to avert danger, while the engine output is optimally controlled.
The AYC and ASC are systems developed as contributions to the enhancement of motor vehicles’ basic performance, namely running, cornering, and stopping to meet the demand of the times for greater car safety. When combined, these systems work for each other to make the vehicle “fun to drive” and achieve much greater safety.
Prev
Next
Established Tokachi Proving Ground.
Established Tokachi Proving Ground.
With the long-term vision of increasing its capability for technological development of high-performance vehicles to establish a stronger research and development framework, Mitsubishi Motors invested the total of 20 billion yen in the construction of the Mitsubishi Motors Tokachi Proving Ground near Otofuke, Kato District, Hokkaido and held a ceremony held a ceremony to celerabrate its compleition at the site.
The Tokachi Proving Ground is built on the premises that measure approximately 1,000 hectares (about 10,000,000 square meters). On the vast tracts of land is an extended elliptical 10-km track, which is ideal as a high-speed circuit. The long radii to the curved edges enable high-speed driving tests at up to 300 km per hour (the highest speed in Japan). This high-standard research and testing ground also boasts a various other facilities, including a test road for braking at high speeds (from 250 km per hour), a 3-km cross country road and a road for testing vehicles in cold temperatures.
A variety of tests are conducted throughout the year, including high speed driving, braking at high speeds and durability in practical. During winter, general tests are conducted on the overall practical function of the vehicle in cold weather.
Prev
Next
1997
Established Shenyang Aerospace Mitsubishi Motors Engine Manufacturing Co., Ltd. in China.
Established Shenyang Aerospace Mitsubishi Motors Engine Manufacturing Co., Ltd. in China.
Mitsubishi Motors received approval from the Chinese government for the establishment of a joint venture for the development, manufacture, and sales of motor vehicle engines and transmissions with four companies, namely the China Aerospace Automotive Industry Group Corporation, the Shenyang Construction Investment Corporation, the Malaysian State China Investment Agency (MCIC Holdings Sdn. Bhd.), and Mitsubishi Corporation. Following this, the Shenyang Aerospace Mitsubishi Motors Engine Manufacturing Co., Ltd. (“Shenyang Aerospace Mitsubishi”) was established in Shenyang, Liaoning Province.
Shenyang Aerospace Mitsubishi launched production in 1998. It supplies engines to not only manufacturers of Mitsubishi brand vehicles, but also to many Chinese manfacturers, in China’s ever-expanding motor vehicle market.
In July 2009, the company fully launched the mass production of the 4A9 engine with the Mitsubishi Innovative Valve Timing Electronic Control (MIVEC*). This lightweight engine has displacement for small vehicles and is environementaly conscious. By offering high-quality products that meet customer needs at just the right time, Shenyang Aerospace Mitsubishi successfully expanded its business.
On May 19, 2017, its engine production totaled up to 5,000,000.
Shenyang Aerospace Mitsubishi is committed to meeting ever-diversifying market needs, enhancing its product lines, and making its products greener, thereby contributing to the development of China’s automotive industry.
* The collective name of Mitsubishi’s variable valve timing technologies
Prev
Next
Payoffs to sokaiya corporate racketeers by the company’s executives were revealed.
Payoffs to sokaiya corporate racketeers by the company’s executives were revealed.
Three executives of Mitsubishi Motors, including a former general manager of the general affairs department, were arrested on suspicion of having violated the Commercial Code (payoffs). They were alleged to have paid an honorarium three times over the years from 1995 and 1997, 9.33 million yen in total, into a bank account held in the name of the wife of a sokaiya corporate racketeer on the pretext of having used a seaside house run by the wife. The money was a payoff for cooperation in the smooth proceedings of general meetings of shareholders.
Then-President Takemune Kimura resigned the following month to take the blame for the incident, and a then-Managing Director Katsuhiko Kawasoe succeeded him as President.
The three executives were indicted in the same month for having violated the Commercial Code (payoffs). They admitted all charges during the trial, and, in April of the following year, the Tokyo District Court rendered suspended sentence of guilty verdict.
Prev
Next
1998
Established the brand message: Ii-mono Nagaku (“Good Products that Last”).
Released mid-term business plan “RM 2001 (Renewal Mitsubishi 2001)”.
Introduced a driving assistance system “Mitsubishi Driver Support System”.
Introduced a driving assistance system “Mitsubishi Driver Support System”.
The Mitsubishi Driver Support System consists of the Lane Departure Warning System, Side-rear Monitor, and Preview Distance Control. The cameras and radar built in the vehicle monitor road and traffic conditions around the vehicle, easing the operational demand on the driver, and alerting the driver so that he/she avoids a lapse of concentration or careless errors, thereby contributing to safe driving. This driver support system was developed to lead the developed as a driving support system that further leads ITS (Intelligent Transport System) technology.
The Preview Distance Control was installed in Diamante, launched in January 1995. The Mitsubishi Driver Support System was first built in the Proudia / Dignity launched in February 2000.
[System Components]
(i) Lane Departure Warning System
The camera on the interior rearview mirror identifies the white line on the road ahead to use sound and visual warnings if it sees that the vehicle will stray from the lane and prompt the driver to correct the way he/she steers by making the steering wheel vibrate.
(ii) Side-rear Monitor
The video cameras installed in the rear of the car body constantly watch the road behind and inform the driver of any approaching vehicle in a blind spot with sound and visual warnings when he/she turns on the blinker, urging him/her to check the road behind.
(iii) Preview Distance Control (inter-vehicle distance control system)
This advanced cruise control system is designed to regulate the throttle and gears according to the inter-vehicle distance from the vehicle ahead measured by the laser radar, maintaining safe inter-vehicle distance. It provides sound and visual warnings to urge the driver to apply the brakes when your following distance is too close to other vehicles.
Prev
Next
Nagoya, Kyoto, and Mizushima Plants acquired ISO 14001 certification.
1999
Introduced direct injection diesel engine (DI Diesel).
Introduced direct injection diesel engine (DI Diesel).
Developed from the IDI diesel engine that burn fuel in the auxiliary combustion chamber embedded in the cylinder head, the direct injection diesel engine (DI diesel) adopts the system for injecting fuel directly into the combustion chamber on top of the piston. This reduces heat loss and improves the intake and exhaust efficiency through a four-valve DOHC, and increases fuel efficiency and output performance by approximately 25 percent each, thereby meets the 2005 fuel efficiency standards for diesel vehicles and long-term emissions control requirements.
The DI diesel was first installed in the Pajero that was launched in September of the same year.
Prev
Next
Issued Environmental Report (currently Sustainability Report).
Entered into equity alliance with Volvo.
Entered into equity alliance with Volvo.
Mitsubishi Motors and Volvo signed a memorandum of agreement to form an equity alliance to develop their stronger cooperative ties in the development, production and sales of trucks and buses around the world. This MOU included the following: MHI would establish an internal company for truck and bus operations in April 2000; a new company would be established by the end of 2001; the truck and bus development, production, and sales operations would be transferred to the new company; and Volvo would acquire 19.9% of the new company's shares.
This memorandum also included the agreement that Mitsubishi Motors would set up an internal truck and bus company in April 2000, establish a new enterprise by the end of 2001, and transfer the bus and truck development, production, and sales business to the new enterprise, and that Volvo would acquire 19.9 percent of shares in the new enterprise.
In December 1999, Mitsubishi Motors and Volvo also entered into an agreement for strategic business alliance based on the memorandum.
In April 2001, Mitsubishi Motors switched to DaimlerChrysler as its partner in a strategic alliance for the truck and bus business. Hence, in June of the same year, The capital alliance between the two companies was terminated when Volvo sold its shares in us.
Prev
Next
Officially certified in the Guinness World Records for a 2,000km drive in 24 hours by its electric vehicle.
Officially certified in the Guinness World Records for a 2,000km drive in 24 hours by its electric vehicle.
Mitsubishi Motors jointly developed a manganese lithium-ion battery with Japan Storage Battery Co., Ltd. (currently GS Yuasa Corporation). The Mitsubishi FTO-EV (prototype) equipped with this battery ran 899 laps around the high-speed test track (2.4 km), 2,142.3 km in total, at the Okazaki Plant over the 24 hours from 8:00 am on December 19, 1999 to 8:00 am on the 20th, becoming the world’s first electric vehicle (EV) to have successfully run 2,000 km in 24 hours.
This isrecord was achieved by a significant reduction in recharging time and improvement in driving range per charge (battery capacity) through the use of a newly developed manganese-based lithium-ion battery as well as a thorough reduction of air resistance in the vehicle itself.
This world record at the time was officially recognized in the Guinness Book of World Records.
Prev
Next
Released mid-term business plan “Heart-Beat 21”.
2000
Established the brand message: Heart-Beat Motors, Mitsubishi Motors.
Agreed on a Capital Tie-up with DaimlerChrysler
Agreed on a Capital Tie-up with DaimlerChrysler
Mitsubishi Motors and DaimlerChrysler AG (hereinafter “DC”) entered into a basic agreement on the business alliance for the design, development, production, and distribution of passenger cars and light commercial vehicles. Under this agreement, DC underwrote new shares to be issued by our company through third-party allotment (34% after the capital increase) for approximately 225 billion yen (450 yen per share), dispatched directors in proportion to the investment ratio, and jointly developed compact vehicles.
On July 28 of the same year, the parties concluded a comprehensive business alliance agreement. However, given the Company's management crisis caused by a series of quality problems, the alliance was strengthened in September, including changes in terms such as a replacement of the president, the dispatch of a chief operating officer (COO) from DC, and a change in the share price (405 yen per share). In October, the two companies completed the procedures to invest 34% of the shares (202.4 billion yen), making DC the largest shareholder of the Company. As a capital support measure, the two companies began cooperation by subscribing to 19.2 billion yen of the Company's convertible bonds.
In 2001, DC acquired 3.3% of the Company’s shares owned by AB Volvo, a former alliance partner of the Company, increasing its stake to 37.3%. which led to the expansion of the relationship between the two companies to include strategic cooperation in the truck and bus business.
The scope of the business alliance involved a wide range of collaborative activities, such as a joint development and production of compact “world cars,” the establishment of Global Engine Alliance, and DC’s dispatch of a design manager from DC.
The capital alliance with DC terminated on November 11, 2005, when DC sold all the shares of Mitsubishi Motors it owned.
Prev
Next
Established Mitsubishi FUSO Truck & Bus Company as an in-house One
Established Mitsubishi FUSO Truck & Bus Company as an in-house One
Following the basic agreement for capital alliance and cooperation with AB Volvo in October 1999 and the business partnership agreement in December 1999, Mitsubishi Motors abolished the Truck & Bus Division and spun off its truck and bus business as the Mitsubishi Fuso Truck and Bus Company.
In July 2000, Mitsubishi Motors concluded a basic alliance agreement with AB Volvo. The contract stipulated that a new company in the truck and bus business would be established by July 2001, and that AB Volvo would invest 19.9% of the capital in the new company.
In April 2001, while preparing for the establishment of the new company, the parties agreed to change Mitsubishi Motor’s strategic alliance partner in the truck and bus business from AB Volvo to DaimlerChrysler AG (currently Mercedes-Benz Group AG), and in the following June, AB Volvo completed procedures for the sale of its shares in Mitsubishi Motors to DaimlerChrysler AG, thereby terminating the alliance between Mitsubishi Motors and AB Volvo.
It was not until 2003 (2003) that Mitsubishi Fuso Truck and Bus Corporation was spun off as a new company
Prev
Next
Quality issues revealed through spot inspection by the Ministry of Transport (currently Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism).
Quality issues revealed through spot inspection by the Ministry of Transport (currently Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism).
Following a whistleblowing by an employee of Mitsubishi Motors to the Ministry of Transport (currently the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism), the head office and Research & Development Center (Okazaki City, Aichi Prefecture) underwent an emergency on-site inspection. It was discovered that the Company had been conducting renovations without submitting notifications regarding recalls and improvement measures, as well as duplicate management of product information communication documents. On July 18, the Company submitted a list of notifications regarding recalls and improvement measures to the Ministry of Transport, admitting that it had concealed information about claims.
Subsequently, on August 22, Mitsubishi Motors submitted 17 notifications on recall (involving more than 600,000 vehicles), 3 notifications on remedial measures, and 5 notifications on service campaigns to the ministry, as well as filing a report on the results of internal investigations.
On August 27, following a series of quality problems, the company was investigated by the Metropolitan Police Department on suspected violation of the Road Trucking Vehicle Act (false reporting), and on September 8, for a series of inappropriate actions involving recall-related operations, the ministry issued an 18-month suspension of nomination and a written notice of censure by the Minister of Transport calling for proper management of recalls.
In addition, the Ministry of Transport filed an accusation with the Tokyo Metropolitan Police Department against Mitsubishi Motors for violating the Road Trucking Vehicle Act (false reporting), and notified the Tokyo District Court to apply a fine of 4 million yen to the Company for concealing recalls.
On October 2, the Company announced the resignation of then-President Katsuhiko Kawazoe taking the responsibility for the crisis and the appointment of Takashi Sonobe as their successor.
Prev
Next
Kawasaki Baseball Team entered the 71st Intercity Baseball Tournament and won the title for the first time.
Partnered with Volvo for the establishment of a new truck & bus company.
Establishment of “Quality Matters Advisory Committee” and “Employee Consultation Office”
Establishment of “Quality Matters Advisory Committee” and “Employee Consultation Office”
In response to the quality problem uncovered in July, the company established three committees: the Quality Investigation Committee, the Quality Response Committee, and the Quality Matters Advisory Committee, to investigate quality issues, compile countermeasures, and audit these issues and countermeasures in order to restore customer confidence and ensure sound management.
1. The Quality Problem Investigation Committee:
The committee was established on July 17, 2000 to investigate the mechanism of cover-ups such as dual management of market defect data (dual-management of the product information reporting system) and other inappropriate activities. Interviews were conducted with more than 50 employees, including former employees, mainly from the quality, development, production, and service departments, who were considered to be involved in the cover-up of market defect data. After the investigation report was submitted to the Ministry of Transport on August 22, this Committee was dissolved.
2. The Quality Response Committee:
The committee was established on August 10, 2000 to implement company-wide measures for improving quality levels in all development, production, sales and after-sales service activities. This work was assigned to four subcommittees: (1) Design & Production Quality; (2) Sales & After-sales Service Quality; (3) Quality Management Organization; (4) Reforms in Quality Awareness. The committees compiled a draft report with proposed measures such as “management of product information reports using a numbering system” and “introduction of an automatic registration system for defect data.” The committee was dissolved on September 30.
3. The Quality Matters Advisory Committee:
The committee, consisting mainly of outside lawyers and other experts, was established: (1) to evaluate and make and make recommendations on quality-issue remedies, (2) to monitor progress in implementation of remedies, and (3) to monitor the running of quality management organization.
The committee met once a month to review the remedial measures and action implemented by the Company. After submitting the Quality Matters Advisory Committee Report to the Company in August 2001, the committee was dissolved.
On the same day, the Employee Consultation Office was established directly under the director in charge of corporate ethics to receive telephone calls, emails, and other correspondence from the Company’s employees, former employees, and employees of affiliated companies and sales companies who sought consultation or make reports. Based on information from employees, the committee then could conduct investigations, propose countermeasures, provide concerned employees with investigation results, and report countermeasures taken.
The Employee Consultation Office continues to function today with outside experts such as lawyers and counselors serving as advisors.
Prev
Next
2001
Released a new business vision “Mitsubishi Motors Turnaround Plan”.
Okazaki Baseball Team entered the 72nd Intercity Baseball Tournament and came second.
Eclipse EV successfully completed the public test run, “Shikoku EV Rally”.
Agree on AT / CVT business integration with JATCO TransTechnology Ltd. (currently JATCO Ltd.)
Agree on AT / CVT business integration with JATCO TransTechnology Ltd. (currently JATCO Ltd.)
With the aim of promoting business concentration under the new management vision "MMC Turnaround Plan" announced in February 2001, MMC, Nissan Motor Co., Ltd. and JATCO TransTechnology Co., Ltd. (currently JATCO Co., Ltd., Fuji City, Shizuoka Prefecture) signed a memorandum of understanding on the AT / CVT business integration between MMC, Nissan Motor Co., Ltd. and JATCO TransTechnology Co., Ltd. (currently JATCO Co., Ltd., Fuji City, Shizuoka Prefecture) to integrate the AT / CVT business of MMC's Kyoto Plant and Mizushima Plant into JATCO TransTechnology Co., Ltd., and started detailed discussions toward the realization of the business integration.
On March 25, 2002, a formal agreement was concluded based on the memorandum, and in April, Mitsubishi Motors spun off its AT/CVT business and incorporated it with Diamondmatic Co., Ltd. (“DMC”), a new company established by the Company. In July, DMC became a wholly owned subsidiary of JATCO Ltd. by exchanging all DMC shares held by Mitsubishi Motors and 18% of JATCO Ltd.’s shares. In April 2003, JATCO Ltd. and DMC merged, completing a series of transactions involving the integration of the Company’s AT/CVT business.
Mitsubishi Motors and JATCO Corporation still maintain a capital relationship and are an important supplier of AT/CVTs used in our company products.
Prev
Next
2002
Fatal accident occurred due to a front tire that came off a Mitsubishi heavy-duty truck.
Fatal accident occurred due to a front tire that came off a Mitsubishi heavy-duty truck.
In Yokohama City, Kanagawa Prefecture, an accident occurred that resulted in the front hub of a heavy-duty truck manufactured by Mitsubishi Fuso (currently Mitsubishi Fuso Truck and Bus Corporation) being damaged, causing a tire to fall off. The tire rolled about 50 meters downhill and struck a mother and three children walking on the sidewalk, fatally injuring the mother.
In June 1992, Mitsubishi Motors learned that there had been cases of front wheel hub failures of its heavy-duty trucks. The Company had since investigated the cause and consequently concluded that it was due to insufficient strength in the design. In 1993, the Company started installing hubs with increased strength in its new vehicles. For vehicles already sold, however, no countermeasures were taken as hubs are parts to be replaced regularly. Although there were subsequent reports of defects in the market, they were dismissed on the grounds that, as long as the wheel nuts were securely tightened and the fastening force remains unchanged, no defects would occur, and no new measures taken in relation to those reports.
The hub failure continued to occur even in the hubs that had already been validated as safe, but no action was taken to address the problem. Furthermore, even though the quality issue that came to light in 2000 was listed as one of the 46 defects identified through an independent investigation by the Ministry of Transport, it was treated as a single defect, and no market measures such as recalls were ever reported.
In October 2004, the Company designated January 10, the day of the accident, as “Safety Pledge Day” in order not to forget the misconduct of prioritizing the Company’s logic and interests over the customer experience.
Prev
Next
Released mid-term environment initiative program “Mitsubishi Motors Environmental Sustainability Plan”.
Established MMC Estec Co., Ltd.
Integrated the 2 channels of domestic distributors.
Fatal accident occurred due to damage in the clutch housing of the a Mitsubishi heavy-duty truck.
Fatal accident occurred due to damage in the clutch housing of the a Mitsubishi heavy-duty truck.
A driver of a heavy-duty truck, manufactured by MMC (currently Mitsubishi Fuso Truck and Bus Corporation), was killed near the Kumage Interchange on the Sanyo Expressway in Yamaguchi Prefecture. The fatal accident was caused by a crack in the clutch housing, resulting in brake hose damage and loss of vehicle control, and sent the driver’s truck crashing into a concrete rampart.
Since 1992, equipment failures associated with the breakage of clutch housings had occurred one after another. After investigating the cause of the problem and reviewing its preventive measures, the Company decided to install an anti-vibration device in its vehicles manufactured in and after 1995. By early 1996, it was found out that the cause of the damage to the clutch housing was due to the design not meeting safety standards and cracks in the manufacturing process. However, due to difficulties in specifying the vehicles with the defective part out of the vehicles that had already been sold, at an internal meeting in May of the same year, the Company decided that they will respond to this issue with repair directives instead of recalls.
Furthermore, another decision was made to make no proactive advise for the customers to bring their vehicles for the refurbishing but to replace the clutch housing only when the vehicles were brought in for checkup or other repairs. In September 1996, repair directives were issued based on this decision.
On top of that, in addition, in a review of defects over the past 2 years in relation to quality problems that were discovered in 2000, the damage to the clutch housing was not considered to be an issue requiring recall.
As with the fatal accident that occurred in Yokohama City, Kanagawa Prefecture, in January of the same year, our company has designated October 19, the day of the accident, as the "Safety Pledge Day " in order not to let this mistake fade away. This misconduct was caused by a lack of customer perspective and prioritizing corporate logic and company convenience.
Prev
Next
Mitsubishi Motors merged Mitsubishi Motors Europe B.V. (MME) with Mitsubishi Motor Sales Europe B.V. (MMSE).
2003
Established Mitsubishi Fuso Truck and Bus Corporation by separating the truck & bus division of Mitsubishi Motors.
Established Mitsubishi Fuso Truck and Bus Corporation by separating the truck & bus division of Mitsubishi Motors.
In December 1999, Mitsubishi Motors spun off its truck and bus business as an in-house company under a strategic business alliance with AB Volvo. But, in April 2001, the Company changed its strategic partner in the truck and bus business from AB Volvo to DaimlerChrysler AG (currently Daimler AG).
In September 2002, Mitsubishi Fuso Truck and Bus Corporation was established as an independent company based on the “Agreement on the Spin-off of Truck and Bus Business and the Purchase and Sales of Shares of a New Company” with DaimlerChrysler AG.
Mitsubishi Motors fully owned the Mitsubishi Fuso Truck and Bus Corporation when it was established, but in 2003, the Company’s ownership decreased to 42% while DaimlerChrysler held 43% and Mitsubishi Group companies 15%. In March 2004, Mitsubishi Motors sold a portion of its shareholding to DaimlerChrysler, bringing its stake to 20%.
On March 10, 2005, based on its agreement with DaimlerChrysler regarding the Mitsubishi Fuso Truck and Bus compensation issue, Mitsubishi Motors transferred the remaining 20% of its shares to DaimlerChrysler, dissolving its capital relationship with Mitsubishi Fuso Truck and Bus Corporation.
Prev
Next
Mitsubishi Motors merged Mitsubishi Motor Manufacturing of America Inc. (MMMA) with Mitsubishi Motor Sales of America, Inc. (MMSA).
Moved the headquarters to Konan, Minato City.
Established a new paint line at Mizushima Plant.
Concluded an agreement for OEM supply of light commercial vehicles with Nissan Motor Co., Ltd.
Changed the company name of MSC to MMTh.
2004
Sold a 22% stake in Mitsubishi Fuso Truck and Bus Corporation to DaimlerChrysler.
2005
Released mid-term business plan “Mitsubishi Motors Revitalization Plan”.
Set up Business Revitalization Monitoring Committee.
Launched the production of 4B1 model engine.
The company filed a lawsuit against a former board member for the compensation of damages related to quality issues.
The company filed a lawsuit against a former board member for the compensation of damages related to quality issues.
An internal investigation into a series of quality issues revealed that, during their tenure, the management officers were responsible for creating a corporate culture and systems that led to such misconduct. Consequently, Mitsubishi Motors filed a lawsuit against seven former board members with the Tokyo District Court, demanding a total of 1,135 million yen in damages.
In addition, the Company requested that 10 former directors and executive officers in the quality assurance, sales, and development departments return a portion of their retirement benefits in proportion to the degree of their responsibility when they were in their position, considering it unnecessary to go so far as to claim a lawsuit.
The lawsuits against those seven board members were settled in 2007.
Prev
Next
Lancer Evolution MIEV won the title in Shikoku EV Rally.
Established the brand message: Kuruma Zukuri no Genten E. (“Pursuing the Origins of Car Engineering”)
Announced the Development of Next Generation Electric Vehicles
Announced the Development of Next Generation Electric Vehicles
From early on, Mitsubishi Motors has been involved in the research and development of electric vehicles as one of the options for next-generation vehicles. It has created test vehicles equipped with high-performance lithium-ion batteries, such as “FTO EV” and “Eclipse EV,” and the Company has been steadily experimenting and developing the vehicle through continuous 24-hour driving tests and public road tests.
Meanwhile, the Company announced a plan to drive forward the development of next-generation electric vehicles, positioning two technologies—“lithium-ion batteries” and “in-wheel motors” which enable a compact drive-train by integrating the motor into the vehicle wheel—as core technologies in its scheme to develop technologies for electric vehicles taking advantage of these features. The Company has named the technologies and vehicles related to this initiative "MIEV (Mitsubishi In-wheel motor Electric Vehicle)" and has announced that it will advance technology development with a view to applying them to hybrid and fuel cell vehicles.
Based on the “MIEV” concept, Mitsubishi Motors developed the Colt EV and the Lancer Evolution MIEV as test vehicles.
The Colt EV, which is based on the Company’s Colt, is equipped with two in-wheel motors mounted on the rear wheels and powered by lithium-ion batteries as the main power source. The Lancer Evolution MIEV, which is derived from the Company’s Lancer Evolution IX, has in-wheel motors mounted on all four wheels and uses lithium-ion batteries as the main power source.
Mitsubishi Motors acquired vehicle type certification for the Lancer Evolution MIEV to allow evaluation not only in the proving ground but also under normal driving conditions on public roads. Specifically, the practicality evaluation of the outer-rotor in-wheel motor was conducted over a wide variety of conditions to examine its reliability and durability when subject to front/rear, left/right, up/down inputs from the road surface, water inundation, exposure to sand and dirt, and other strains. While continuing to conduct public road tests and charging tests, Mitsubishi Motors entered a Lancer Evolution MIEV test vehicle in the Shikoku EV Rally 2005 held on August 27 and 28, 2005 in Tokushima Prefecture in order to promote the MIEV concept to the general public.
To date, the Company has not sold vehicles equipped with in-wheel motors. However, the accumulation of technologies developed and researched based on the "MIEV" concept has been a major turning point in its current electrification path.
Prev
Next
Announced that the company suspended its official participation in World Rally Championship.
2006
Established Lingfa Car Technical Consulting (Shanghai) Ltd. in China.
Launched the production of 6B3 model engine.
Announced Environment Initiative Program 2010.
Acquired shares in South East (Fujian) Motor Co., Ltd. of China.
Acquired shares in South East (Fujian) Motor Co., Ltd. of China.
On December 28, 2004, to step up its production and sales organization capabilities in the Chinese market, Mitsubishi Motors signed a memorandum of understanding with China Motor Corporation (Taipei, Taiwan; hereinafter “CMC”) on expanding the business operations of South East (Fujian) Motor Co., Ltd. (Fujian, China; hereinafter “SEM”), a subsidiary of CMC.
On April 12, 2006, Mitsubishi Motors concluded agreements with China Motor Corporation and Fujian Motor Industrial Corporation on taking a direct equity interest in South East (Fujian) Motor Co., Ltd. (SEM), based on which, on September 28, 2006, the Company completed procedures for investing in SEM.
Mitsubishi Motors has licensed its technologies to SEM since 1995. Following this investment, SEM commenced the production and sales of the Lancer and Space Wagon for the first time under the Mitsubishi brand, followed by Galant models in November. The goal was to strengthen Mitsubishi Motor’s brand strategy and expand its model lineup in China.
While the Company maintains a capital relationship with SEM continues with its 25% stake in SEM as of the end of fiscal 2018, SEM’s production of Mitsubishi brand vehicles ended in 2017.
Prev
Next
Initiates “Pajero Forest & Local Mountain Restoration Initiative”
Initiates “Pajero Forest & Local Mountain Restoration Initiative”
Commemorating the launch of the fourth-generation Pajero, Mitsubishi Motors began an initiative to conserve and cultivate Japan’s forests and woodlands the condition of which are deteriorating on a wide scale. The initiative is based in Suzurishima Property Ward’s mountain forest in Hayakawa-cho, which lies in the foothills of the Southern Japanese Alps in Yamanashi Prefecture. The three-hectare area of mountain forest there was named “The Pajero Forest.” On November 30, 2006, the Company signed a memorandum for the “Pajero Forest & Local Mountain Restoration Initiative” with the town of Hayakawa through the cooperation of Yamanashi Prefecture and the OISCA Japan Foundation, * which has a proven track record in environmental protection activities. The opening ceremony for the initiative was held in June 2007 before the Company’s employee volunteers began their activities to protect the forest, such as tree planting and underbrush clearing.
The activities were carried out every year except for the years when they were cancelled due to bad weather until the area was devastated by Typhoon No. 4 in 2012, which made the activities impossible.
In 2014, Hayakawa Town donated approximately 7.23 hectares of forest in the Yushima area, which will become a new site for the project. On September 17, the Company signed a memorandum for the second phase of “Pajero Forest & Local Mountain Restoration Initiative” and committed to promoting the activities to protect the forest over the next 10 years. The forest protection activities continue to this day based on this memorandum.
Note: The OISCA Japan Foundation is an international cooperation NGO established in 1961 with its headquarters in Tokyo works mainly in the Asia-Pacific region with a key aim of fostering human resources through agriculture and forestry.
Prev
Next
Attended KidZania Tokyo as an exhibitor.
Urawa Red Diamonds won the J-League for the first time.
2007
Separated Mitsubishi Auto Credit-Lease Corporation into two companies.
Moved the headquarters to Shiba, Minato City.
Started Experiments with a Power Company to Evaluate the performance of Electric Vehicle “i-MiEV”
Started Experiments with a Power Company to Evaluate the performance of Electric Vehicle “i-MiEV”
Mitsubishi Motors announced that an i-MiEV test vehicle was delivered to both Tokyo Electric Power Co., Inc. (hereinafter “TEPCO”) and Kyushu Electric Power Co., Inc. (hereinafter "Kyushu Electric Power") through a joint research project on the development of a next-generation electric vehicle (EV)—MiEV (Mitsubishi innovative Electric Vehicle) for the electric power companies to confirm the suitability of the new EV as a business vehicle and its compatibility with a quick-charging infrastructure.
This performance evaluation was the first stage of the joint research, and the Company evaluated the compatibility with the fast charger developed by TEPCO and the suitability as a business vehicle (Range, power performance, usability, etc.), and it was confirmed that sufficient performance was secured.
In February 2008, as the second phase of the joint research, the Company delivered to TEPCO a total of 10 i-MiEV verification test vehicles with improved batteries, motors, and other key components of EVs that increased their cruising range.
For the verification running tests, Mitsubishi Motors supplied test vehicles and analyzed the test data, while TEPCO deployed i-MiEVs at its branch offices and other locations and collected data from the test runs, evaluating their practicality for use as business vehicles, in order to assess the overall performance in actual operating environments and the market acceptability.
Similar verification tests were conducted with the Kyushu Electric Power Co., Inc., Kansai Electric Power Co., Inc., Chugoku Electric Power Co., Inc., Okinawa Electric Power Co., Inc., Hokkaido Electric Power Co., Inc., Hokuriku Electric Power Company, and overseas electric power companies and governments as part of preparations for the market launch of the i-MiEV.
Prev
Next
Established MMC Wing Co., Ltd.
Established MMC Wing Co., Ltd.
The Company established MMC Wing Inc. as a wholly owned subsidiary to promote the employment of people with disabilities. On October 25 of the same year, the new company was officially recognized by the Minister of Health, Labor and Welfare as a special subsidiary company.*
The company’s employees collect, sort, and send mail; collect recyclable waste and sort it for recycling; assemble automotive components; package and label parts; and engage in greening activities.
Note: A special subsidiary company is a subsidiary established in accordance with the provisions in Article 44 of the Act to Facilitate the Employment of Persons with Disabilities and approved by the Minister of Health, Labor and Welfare.
Prev
Next
Integrated the 29 affiliated domestic distributors into 5 companies.
Established Mitsubishi Automotive Logistics Technology Co., Ltd.
Established Mitsubishi Automotive Logistics Technology Co., Ltd.
Mitsubishi Automotive Logistics Technology Co., Ltd. was established by integrating Mitsubishi Automotive Logistics Co., Ltd., a company engaged in the transportation of finished vehicles, and Mitsubishi Automotive Techno-Service Co., Ltd., a company engaged in vehicle inspection and maintenance.
The two companies were integrated as part of the elimination and consolidation of affiliated companies that had been undertaken since the first year of the Business Revitalization Plan. This integration enabled a centralized management of vehicle transportation, inspection, and maintenance operations.
The history of Mitsubishi Automotive Logistics Co., Ltd. dates back to July 1979, when Daiya Automotive Transportation Co., Ltd. was established through a merger of Ryowa Automotive Transportation Co., Ltd. and Ryoto Shipping Co., Ltd. The new company served as a general contractor for transportation services, including domestic land/sea transportation and export shipping of Mitsubishi Motor products. The company name was changed to Mitsubishi Automotive Logistics Co., Ltd. in July 1991. Mitsubishi Automobile Techno Service Co., Ltd., was established in October 1990 after changing its name from Shinryo Automobile Maintenance Co., Ltd., which oversaw inspection and maintenance of new vehicles at distribution centers around the country.
Zero Co., Ltd. has been in charge of transportation of Mitsubishi Motors’ completed vehicles since July 2019, whereas Mitsubishi Automotive Logistics Technology Co., Ltd. sells parts and accessories, inspects new vehicles, and engage in remanufacturing operations for Mitsubishi Motors.
Prev
Next
Introduced automatic manual transmission “Twin Clutch SST”.
Introduced automatic manual transmission “Twin Clutch SST”.
Mitsubishi Motors developed the Twin Clutch SST (Sport Shift Transmission), which enables more agile gear shifting than manual transmission.
In general, shifting gears in a manual transmission requires clutch operation and gear operation with the shift lever, whereas the Twin Clutch SST enables lag-free gear changes by automatically switching each clutch because it features two separate clutch systems, one for odd gears (1st, 3rd and 5th gears) and the other for even gears (2nd, 4th and 6th gears).
In addition, transmitting power with clutches instead of a torque converter makes the Twin Clutch SST simpler in structure and reduces power transmission losses for higher transmission efficiency that leads to improved fuel mileage.
Moreover, the three speed change programs below are available to suit the driving scene, and the system can be used for a wide range of driving from city riding to winding running.
Normal mode:
This mode is for normal driving situations. Normal mode scheduling uses relatively low-speed shift points to deliver unobtrusive shifting for maximum comfort together with optimum fuel economy.
Sport mode:
This mode is used for more demanding driving or when engine braking is required. Sport mode scheduling uses higher shift points and quicker shifting to deliver instant throttle response.
S-Sport mode:
Compared with Sport mode, S-Sport mode scheduling keeps the engine turning at higher revs while allowing lightening-fast shifting.
The Twin Clutch SST was first introduced in the Lancer Evolution X launched on October 1, 2007.
Prev
Next
Introduced integrated vehicle dynamics control system “S-AWC”.
Introduced integrated vehicle dynamics control system “S-AWC”.
Mitsubishi Motors developed S-AWC (Super All Wheel Control), a system that integrates control of vehicle motion centered on the control of driving and braking forces to all four wheels, and first installed it in the Lancer Evolution X, which went on sale on October 1, 2007.
The S-AWC system integrates the management of all its AYC, ACD, ASC and Sport ABS components while adding braking force control to Mitsubishi Motors' own AYC system. As a result, the S-AWC elevates drive power, cornering performance as well as vehicle stability under all driving situations, from everyday motoring to emergency evasion maneuvers.
[System description]
(1) Active Yaw Control (AYC)
The AYC controls the rear wheel torque differential according to driving conditions to limit the yaw moment that acts on the vehicle body and enhance cornering performance. This new technology also acts like a limited slip differential (LSD) by suppressing rear wheel slip to improve traction.
AYC was adopted for the first time in the world in the Lancer Evolution IV launched in August 1996. It then took an evolutionary step forward in the Lancer Evolution VIII launched in January 2003 as the Super AYC doubling the torque transmission capacity by revising the differential system.
(2) Active Center Differential (ACD)
For different driving conditions, this system regulates the differential limiting action between free and locked states to optimize front/rear wheel torque split, thereby realizing higher levels of steering response and traction at the same time.
(3) Active Stability Control
This system stabilizes vehicle attitude while maintaining optimum traction by precisely regulating engine power and the braking force at each wheel. It improves traction under acceleration by preventing the driving wheels from spinning on slippery surfaces. It also elevates vehicle stability by suppressing skidding in an emergency evasive maneuver or the result of other sudden steering inputs.
(4) Sport Anti-lock Brake System
This system allows the driver to maintain steering control and keeps the vehicle stable by preventing the wheels from locking under heavy braking or when braking on slippery surfaces. The addition of yaw rate sensors and brake pressure sensors to the ABS system has improved braking performance through corners.
Prev
Next
Established Lithium Energy Japan.
Established Lithium Energy Japan.
In May 2007, Mitsubishi Motors began talks with GS Yuasa Corporation (hereinafter “GS Yuasa”) and Mitsubishi Corporation (hereinafter “MC”) over the establishment of a joint venture to manufacture large-capacity and high-performance lithium-ion batteries ideally suited for electric vehicles, and agreed to establish Lithium Energy Japan (hereinafter “LEJ”) on the premises of GS Yuasa’s head office in Kyoto with a 15% stake held by Mitsubishi Motors, 34% by MC, and 51% by GS Yuasa Power Supply, Ltd.
GS Yuasa secured a plant site and building for LEJ in Kusatsu City, Shiga Prefecture on July 31, 2008, and LEJ took the land and building on lease and built its Kusatsu Plant, the world's first plant for mass production of large-capacity lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles. From June 2009, the plant began to produce 200,000 cells (enough for approx. 2,300 EVs) annually of the Company's "LEV50 (cell capacity: 50Ah)" lithium-ion batteries. These batteries were installed in the next-generation electric vehicle "i-MiEV," launched in July. The second line began operations in April 2010, enabling LEJ to ship an additional 400,000 cells.
On July 9, 2011, LEJ moved its headquarters to a new plant in Ritto City, Shiga Prefecture, to further expand its business scale.
Prev
Next
2008
Released mid-term business plan “Step Up 2010”.
Announced the closure of the vehicle assembly plant of Mitsubishi Motors Australia Limited (MMAL).
Established the brand message: Drive@earth.
2009
Established Mitsubishi Motor Sales (China) Co., Ltd. in China.
Announced that the company stopped its official participation in Dakar Rally.
Attended KidZania Koshien as an exhibitor.
Announced “Mitsubishi Motors Group Environmental Vision 2020”.
Concluded an agreement to supply OEM electric vehicle “i-MiEV” to PSA.
Established Kansai Electric Vehicles Association.
Established Kansai Electric Vehicles Association.
Mitsubishi Motors signed a memorandum with Mitsubishi Corporation, Mitsubishi Auto Leasing Corporation, and The Kansai Electric Power Co., Inc. to establish the “Kansai Electric Vehicle Promotion Council” with the aim of promoting the use of electric vehicles in the Kansai region. The Council is now comprised of six companies, including Toyota Motor Corporation and Honda Motor Co., Ltd.
The Council contributes to the realization of a low-carbon society by implementing initiatives to promote the use of electric vehicles and develop recharging infrastructure in cooperation with councils and local governments in the Kansai region, including Osaka Prefecture, Kyoto Prefecture, Fukui Prefecture, and Kyoto City, where such initiatives are already underway.
Prev
Next
2010
Established CHAdeMO Association.
Established CHAdeMO Association.
With the aim of expanding the number of locations for quick charging and standardizing the charging method, which are indispensable for further promotion of electric vehicles, the CHAdeMO Association was established by a group of five lead companies—the Toyota Motor Corporation, Nissan Motor Co. Ltd., Mitsubishi Motors Corporation, Fuji Heavy Industries Ltd., and Tokyo Electric Power Co., Inc. The then-chairman of the Tokyo Electric Power Co., Inc., was inaugurated as the first president of the association. It has now been joined by 158 companies and groups as regular members or supporting members, including 19 foreign companies, from multiple sectors such as automakers, electric utility companies, charger manufacturers, and charging service providers.
Through technological improvement of quick chargers and standardization of charging methods, as well as global diffusion of knowledge on quick charger infrastructure developed in Japan from the perspective of international contribution, CHAdeMO strives to promote the spread of electric vehicles (including plug-in hybrid vehicles), which will contribute greatly to the reduction of emissions from the transportation sector.
CHAdeMO, a trademark name for a quick charger developed to promote standardization, is an abbreviation of “CHArge de MOve” (“charge for moving” in English), is derived from the Japanese phrase “Ocha demo ikagadesu ka,” which translates to “How about some tea?,” referring to the time it would take to charge a car. In addition, “de” in CHAdeMO implies “denki,” which means electricity in Japanese. The logo mark is a combination of the circuit symbol for a cell and a curved line indicating “move,” which creates a smiley face that evokes a bright future and sense of happiness, and the color of the logo is green, representing ecology.
Prev
Next
Established a Vehicle Assembly Plant in Collaboration with PSA in Russia
Established a Vehicle Assembly Plant in Collaboration with PSA in Russia
On July 11, 2005, Mitsubishi Motors and PSA Peugeot Citroën (hereinafter “PSA”) concluded an agreement to start a collaborative project to supply PSA with 30,000 units annually of new SUVs* developed and based on a new Mitsubishi platform (vehicle body).
This collaboration was beneficial to both companies, as it allowed Mitsubishi Motors to significantly improve productivity by increasing the operation rate of its production plants, as well as providing PSA with opportunities to attract new customers in the expanding SUV market by enhancing its SUV lineup under both the Peugeot and Citroën brands.
Mitsubishi Motors concluded an agreement with PSA to supply diesel engines in January 2007, followed by a basic agreement with the company in September 2009 for the development and supply of the “i-MiEV,” a new-generation electric vehicle that the Company had been selling in Japan, thus expanding its business collaboration with PSA.
Against the backdrop of the collaborative relationship, in May 2008, Mitsubishi Motors and PSA signed a basic agreement for a joint venture to produce vehicles in Russia as a new collaborative project, and with a capital ratio of 30:70 for Mitsubishi Motors and PSA respectively, the construction of a joint vehicle assembly plan began in Kaluga, Russia in June 2007 and was completed on April 23, 2010.
The launch of the new plant was a major step toward strengthening the automobile market in Russia as well as expanding sales in the market, where demand was expected to recover.
This plant began semi-knockdown production of the Peugeot 308 in the same month, gradually increasing the number of models produced by both companies, and full-scale production began in July 2012 (2012). It still holds an essential position in the Company as a production base for European specification vehicles.
Mitsubishi vehicle models produced at this plant: Outlander, Pajero Sport
Note: The Outlander is called Peugeot 4007 under the Peugeot brand and Citroen C-Crosser under the Citroen brand.
Prev
Next
Participated in the “next generation EV” project.
Participated in the “next generation EV” project.
The City of Kyoto, Nissan Motor Co., Ltd., HORIBA, Ltd. and Mitsubishi Motors launched the Kyoto Next-Generation Electric Vehicle Project, a joint initiative to promote an increased use of electric vehicles, develop a car-use system suited to traffic conditions, and enhance eco-driving, and concluded an agreement for the project. To achieve a low-carbon society, Kyoto City—an environmental model city as well as the birthplace of the Kyoto Protocol—has strived to promote the city as a “Walking City” and popularize and promote next-generation vehicles such as EVs.
The initiative included the promotion of the use of electric vehicles, development of a car-use system suited to Kyoto's traffic conditions, and promotion of environmentally friendly driving and eco-driving. In addition, various conducted various implementation experiments., including the holding of an EV symposium and “E1 Grand Prix,” an eco-driving competition on the Kyoto City Eco-driving website managed by the city.
The agreement was terminated on December 24, 2019 as it was recognized that the project had played a certain role in achieving the goal of the agreement—building a low-carbon society in the transportation sector and promoting the use of public transportation in Kyoto, leading to further expansion of such efforts across Japan.
Prev
Next
Launched the sale of electric vehicle “i-MiEV” through home appliance retailers and online shopping.
2011
Released mid-term business plan “Jump 2013”
Started Verification Tests of Secondary Use Business Model for lithium-ion Batteries
Started Verification Tests of Secondary Use Business Model for lithium-ion Batteries
GS Yuasa Corporation (hereinafter “GS Yuasa”), Mitsubishi Corporation, Lithium Energy Japan (hereinafter “LEJ”), and Mitsubishi Motors conducted tests to verify the effectiveness of the secondary utilization of used lithium-ion batteries from electric vehicles (hereinafter “EV”) at the Lawson Kisshoin Satominami store in Minami-ku, Kyoto. This was the first implementation experiment project of its kind in Japan, where lithium-ion batteries that had been installed in an i-MiEV were used for the tests.
Specifically, in the implementation experiment, electricity generated by solar power was stored in LEJ's “LEV50” lithium-ion batteries from an i-MiEV vehicle, using the “PV-EV System” developed by GS Yuasa, and the electricity was then quickly charged to an EV using GS Yuasa's EVC-20KD quick charger for EVs. The main feature of this system is that a quick charger can be installed without additional investment in power receiving and distribution facilities or any changes to power contracts. EVs that run on power generated from natural energy will enable zero emissions from power generation to driving vehicles.
Furthermore, building a disaster-resilient back-up power system for power outages enables charging EV with solar power as well as supplying electricity from an emergency outlet during power outages. Following the field tests, on November 21, 2011, GS Yuasa launched “PV-EV System,” a quick EV charging system.
Prev
Next
Established NMKV Co., Ltd.
Established NMKV Co., Ltd.
In August 2003, Mitsubishi Motors cand Nissan Motor Co., Ltd. (Nissan Motor Co., Ltd.) entered into a product supply agreement in August 2003 (2008) under whose OEM contract Nissan supplied light commercial vehicles to Nissan Motor Co., Ltd. In 2005, Nissan began supplying light passenger vehicles to Nissan Motor Co., Ltd., and in 2007, Nissan began supplying light commercial vehicles to Nissan Motor Co., Ltd and then expanded OEM supply between the two companies.
Based on a business cooperation agreement signed on December 14, 2010, Mitsubishi Motors and Nissan formulated a project for the establishment of a 50:50 joint venture specializing in product planning and development of “Kei-cars” or mini vehicles for the Japanese market, and on May 19, 2011, reached an agreement to launch a new company with a 50:50 investment ratio.
On June 20, 2011, NMKV Co., Ltd. (hereinafter “NMKV”), a new joint venture formed by Nissan and Mitsubishi Motors, announced an overview of its future business plans as follows: NMKV would integrate the product planning and engineering of future mini vehicles for Nissan and Mitsubishi in the Japanese market by harnessing the product planning know-how possessed by each company. It was integrated the strengths of Nissan and Mitsubishi in the areas of vehicle engineering, development and parts sourcing, as part of an overall strategy to bring new mini vehicle products to market.
Mini vehicles to be designed and developed by NMKV:
- 3rd Generation eK Wagon (Nissan brand: DAYZ)
- 1st Generation eK SPACE (Nissan brand: DAYZ ROOX)
- 4th Generation eK Wagon (Nissan brand: 2nd-generation DAYZ)
- 1st Generation eK Cross (Nissan brand: DAYZ Highway STAR)
Prev
Next
Introduced an idling-stop function “Auto Stop & Go (AS&G)”
Introduced an idling-stop function “Auto Stop & Go (AS&G)”
Auto Stop & Go (AS&G) is an idle-stop mechanism that reduces fuel consumption by automatically shutting off the engine when the car is stopped at traffic lights.
When the launching of the mechanism was announced in Japan, it had already been employed on some manual transmission models for the European market, including the ASX (RVR in Japan) and the Lancer (Galant Fortis in Japan). Then, a new version of AS&G system was developed for use on models fitted with continuously variable transmissions (CVTs). The addition of a new control unit (the AS&G ECU) to vehicle management systems means that the new AS&G is also integrally controlled along with existing systems such as the engine, CVTs, Active Stability Control (ASC) and climate control.
Combining AS&G to the new MIVEC engine provides quick engine restart and initial acceleration performance that feels no different from a car without AS&G. The new AS&G also controls brake force from engine stop to restart via the car's integrated control system. This means that the car will remain stopped on inclines until power is applied to the wheels.
On January 20, 2015, the Company announced their promotion of the “Mitsubishi Motors Environment Initiative Program 2015” as one of the key points of its mid-term management plan “Jump 2013,” setting a target of reducing emissions per vehicle (new vehicle) during driving, by 25% in comparison from FY2005 levels as a global average. In addition, the “Mitsubishi Motors Group Environmental Vision 2020” set a target of achieving a 50% reduction compared to FY2005 levels.
Based on these targets, the Company is developing and commercializing electric vehicles such as plug-in hybrids, actively engaging in the development of technologies to improve the fuel efficiency of internal combustion engines by adopting the AS&G system and other technologies.
On October 20, 2011, Mitsubishi Motors announced the development of the then latest version of AS&G, which was installed on a partially remodeled RVR for the first time in Japan.
Prev
Next
Participated in the Yui Project, an initiative to support the victims of the 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake
Participated in the Yui Project, an initiative to support the victims of the 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake
In the aftermath of the Great East Japan Earthquake, Mitsubishi Motors has provided support to the disaster-stricken areas in a variety of ways, including donations, the loan of the i-MiEV electric vehicle to the disaster-stricken areas, and active recruitment of high school students in the disaster-stricken areas. As a further support activity, the Company has participated in Project Yui, a public-private partnership consortium to support disaster-stricken areas.
At the beginning of the project, the Company recruited participants through internal recruitment, and mainly in Ishinomaki City, Miyagi Prefecture, sorted and delivered educational materials, supported children's learning and play activities such as sports, drawing, playing pictures with children in temporary housing and schools.
Since then, in response to ongoing requests for support due to the expansion of activities, such as the operation of temporary childcare facilities in line with the reconstruction situation in May 2013, the Company launched a “Drink and Donate” program, which donates part of the proceeds from purchases made from in-house vending machines to fund the activities of “YUI no Ie,” a day-care and childcare facility for school-age children operated by the project. The total amount donated through the program reached approximately 13.6 million yen.
Mitsubishi Motors agreed with the philosophy of the project and thus continued support for it, but in December 2018, the Company discontinued our support due to the assumption that it had achieved its initial objective of providing support for the recovery of disaster-affected areas after seeing that the project had shifted from the phase of recovery to that of self-support and that the operation of “YUI no Ie” had been taken over by a local company.
The “Drink and Donate” program is still ongoing and provides donations to the MICHINOKU Future Fund, a public interest incorporated foundation.
Prev
Next
2012
Established a new paint line at Nagoya Plant.
1500 W power supply system MiEV power BOX launched
1500 W power supply system MiEV power BOX launched
Mitsubishi Motors launched the sale of 1500W power supply unit “MiEV power BOX.” Supplied by its affiliated sales agents nationwide, the power feeder, which enables the extraction of large amounts of power from electric vehicles was offered as a dealer option for the Company's i-MiEV and MINICAB-MiEV electric vehicles. The Company lent i-MiEV electric vehicles to the areas affected by the Great East Japan Earthquake as part of our support initiatives, and based on the experience, it developed this unit to meet the demand for electricity in areas undergoing sluggish restoration work.
The MiEV power BOX is an adapter that plugs into the i-MiEV or MINICAB-MiEV's quick charging connector and is a device that can extract part of the power stored in the large capacity driving battery up to 1500W at 100V AC. When connected to a fully-charged 16.0 kWh battery-equipped model the MiEV power BOX can supply 1500 watts of power for between five and six hours, equivalent to the amount consumed by an average household in a single day.
Much attention is focused on the storage capabilities of high-capacity EV batteries as a power source for use in major disasters and other emergencies, which was the original intention of the development of the unit. This comes at a time when solar power, wind power, and other recyclable energy sources are being promoted and the implementation of "smart grids" which will allow the more effective use of electrical power. More and more people are looking to EV both in terms of its traditional role of addressing environmental issues and as a means of addressing ever-growing pressures on the demand and supply of energy. As for meeting these expectations, the Company continues to promote research and development of related technologies for electric vehicles, including the MiEV power box.
Prev
Next
Established a new EV Research & Development Center.
Introduced a preventative safety technology “e-Assist”.
Introduced a preventative safety technology “e-Assist”.
e-Assist is a preventive safety technology that utilizes radio wave radar * 1 and cameras * 2 to support safe and comfortable driving. It consists of three functions: the Radar Cruise Control System (ACC), which maintains the distance between the vehicle and the preceding vehicle while driving; the Collision Damage Reduction Brake System (FCM), where automatic braking is used to help avoid a collision or reduce damage when the distance between the vehicle and the preceding vehicle is reduced; and the Lane Departure Warning System (LDW), which alerts the driver when the vehicle is about to deviate from the driving lane. This technology assists the driver to drive safely in relatively accident-prone situations, such as long-distance driving, nighttime driving, and bad weather.
In addition, the latest e-Assist is equipped with the Misacceleration Mitigation System that further enhances prevention safety.
The Company is proactively adopting safety and security equipment in its commercial vehicles, such as e-Assist, the Reinforced Impact Safety Evolution (RISE), SRS airbags, and Active Stability Control (ASC), which suppresses vehicle skidding.
The e-Assist system was installed for the first time on the fully redesigned Outlander SUV which was released in October 2012 in Japan.
Notes:1. Radar unit
The radar unit is mounted behind the front grill and monitors the distance to and relative speed of the vehicle in front. It is a 77GHz millimeter-wavelength radar unit that provides highly reliable and stable performance regardless of direction of sunlight or other light, driving in rain or at night, with a maximum detection range of around 200 meters.
2. Camera unit
The camera unit is mounted at the top of the front windshield and monitors the position of the lane dividing lines in front of the vehicle. To prevent fogging of the lens and maintain precise and consistent imaging quality, the unit is mounted directly to the windshield inside the vehicle.
Prev
Next
Established GAC Mitsubishi Motors Co., LTD. (GMMC) in China.
Established GAC Mitsubishi Motors Co., LTD. (GMMC) in China.
GAC Mitsubishi Motors Co., Ltd., a joint venture of Guangzhou Automobile Group Co., Ltd., Mitsubishi Corporation, and Mitsubishi Motors Corporation, holding a stake of 50%, 17%, and 33% respectively, was established. The new company began operations on the day of its establishment.
Commencing the production of the ASX (RVR in Japan) from October 2012, the Pajero Sport (for overseas only) in 2013, the Outlander in 2016, and the Eclipse Cross in 2018, GMMC plays an important role in China as a finished vehicle plant.
Prev
Next
Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism conducted spot inspection at the company following leaking engine oil trouble in Kei-cars.
Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism conducted spot inspection at the company following leaking engine oil trouble in Kei-cars.
In 2005, Mitsubishi Motors reported incidents of faulty crankshaft oil seals on its mini vehicles falling off, and from that time, the same problem recurred frequently. Following ongoing guidance from the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism, the Company filed a recall on November 11, 2010. The Company issued a second recall on January 26, 2012 to extend the recall period, and a third recall on March 19 to increase the coverage of vehicles under the recall because, in the previous recall notice, there was an error in selecting the vehicles to be covered by the recall.
On December 19, 2012, the Company issued a fourth recall to further expand the scope of the recall, and submitted to the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism a report on the results of an internal investigation examining the issues concerning the recall notices issued so far.
Following the results of the report, the MLIT issued a strict verbal warning to Mitsubishi Motors and conducted an on-site inspection at the company from December 25 until 27, 2012.
Though no legal or regulatory violations were found during the on-site inspection and related investigations, the same defects continued to be detected and the Company remained passive in the handling of the recalls. Its attitude is to be blamed from the perspective of compliance as well as in terms of “Customer First.”
Prev
Next
2013
Supported the Michinoku Future Fund, a scholarship fund for the orphans of earthquake disaster.
Supported the Michinoku Future Fund, a scholarship fund for the orphans of earthquake disaster.
The “Mitsubishi Motors STEP Funds,” established by the Company’s employee volunteers, offered support for the recovery from the Great East Japan Earthquake by making donations through the Japan Committee for UNICEF to the Great East Japan Earthquake Emergency Fund. After the fund was closed upon achieving its purpose, Mitsubishi Motors chose the MICIHNOKU Future Fund, a scholarship fund for students wishing to continue their studies, as a new destination for its donations in the hope that children, the cornerstones for the recovery from the disaster, would grow without abandoning their dreams and objectives and play key roles in the recovery of their hometowns.
The fund provides scholarships to students who lost one or both parents in the Great East Japan Earthquake and wish to advance to university, junior college, or technical school. It is a very long program that lasts for a quarter of a century until the age of 0 in the year of the Great East Japan Earthquake graduates from college.
As of the end of 18, the total amount of donations to the fund was approximately 15 million yen. On March 11, 2016 (2016), we donated 1 Delica D: 5 to the fund in response to its request for use in transportation for children in the Tohoku region.
Prev
Next
Released mid-term business plan “New Stage 2016”.
2014
Cancellation of Preferred Shares
Cancellation of Preferred Shares
Facing a crisis that called into question its very existence due to a decline in sales volume in the U.S., an increase in sales promotion expenses, and losses in the sales finance business as well as deterioration in its creditworthiness caused by the recall issues, Mitsubishi Motors announced the Business Revitalization Plan on May 21, 2004 and issued preferred shares to Mitsubishi Group companies, including Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd., Mitsubishi Corporation, The Bank of Tokyo-Mitsubishi, Ltd. (currently The Bank of. Tokyo-Mitsubishi UFJ, Ltd.), The Mitsubishi Trust and Banking Corporation (currently The Mitsubishi UFJ Trust and Banking Corporation) as major underwriters.
However, the rehabilitation funds had to be used to repay interest-bearing debt and other liabilities, resulting in a rapid shortage of funds. On January 28, 2005, the Company announced the Mitsubishi Motors Revitalization Plan as a new capital reinforcement measure, issuing common and preferred shares to three Mitsubishi Group companies: Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd., Mitsubishi Corporation, and The Bank of Tokyo-Mitsubishi, Ltd. to further increase its capital levels.
Subsequently, the Company's performance and financial position improved due to financial support from Mitsubishi Group companies and other sources. As a result, the Company’s ordinary income and net income reached record highs in FY2012, clearing the accumulated losses in 2013.
In November 2013, Mitsubishi Motors released the Capital Restructuring Plan to acquire and dispose of all preferred shares through a public offering of common stock and to resume dividends to its common shareholders. At an extraordinary general meeting of shareholders held in December 2013, the resolution to cancel the preferred shares was approved, which enabled the Company to pay dividends to its common shareholders at the end of FY2013 for the first time in 16 years.
Prev
Next
Sponsorship of the Great Forest Wall Project, a tree planting volunteer initiative
Sponsorship of the Great Forest Wall Project, a tree planting volunteer initiative
Since the occurrence of the Great East Japan Earthquake, Mitsubishi Motors has continued to support the reconstruction of the disaster-stricken areas in a variety of ways, including lending the i-MiEV electric vehicle to the disaster-stricken areas and actively recruiting high school students in the disaster-stricken areas.
Following these activities, in support of the "The Great Wall of the Forest Project (Current Chinju Forest Project)" which aims to support areas affected by the Great East Japan Earthquake, the Company lent five MINICAB-MiEV TRUCK electric vehicles free of charge.
Those vehicles were used to transport saplings and water tanks for the project's tree-planting initiative “The 2nd Millennium Hope Hills Tree Planting Festival 2014 in Iwanuma City, Miyagi Prefecture - Planting 100,000 Trees for Children 1,000 Years from Now,” held on May 31. The event was joined by Tohoku Mitsubishi Motors Sales Co., a local car dealership, in order to charge electricity to the vehicles. On June 14, the Company’s employee volunteers participated in the project’s initiative of planning trees along coastal lines—“Inochi wo Mamoru Mori no Bochotei,” which translates to “Forest Coastal Levees That Protect Lives.”
Prev
Next
Established Nippon Charge Service LLC (NCS).
Nagoya Plant achieved production of a cumulative total of 5 million units.
2015
Establishes MMKI in Indonesia
Establishes MMKI in Indonesia
Positioning the ASEAN region as its most important market, Mitsubishi Motors has embarked on a range of new projects under its New Stage 2016, medium-term management plan announced in 2013, including the production of the all-new Triton pick-up truck in Thailand and the launch of production at a new assembly plant in the Philippines with a view to achieving sustainable growth and enhance corporate value. In the medium-term management plan "New Stage 2016" announced in 2013 (2013), the Company identified the ASEAN region as the most important market to achieve "sustainable growth as well as "enhancement of corporate value, "establishing new projects such as the full model change of Triton in Thailand and the start of production at a new plant in the Philippines.
In Indonesia, which has the fourth largest population in the world and where the demand for vehicles is expected to increase as the economy continues to grow, the Company’s motor vehicles have been manufactured and sold since 1970. The cumulative total of light commercial and passenger vehicles reached 1.3 million as of the end of 2014. The growing sales in the country led to the establishment of Mitsubishi Motors Krama Yudha Indonesia (MMKI), a joint venture established through a partnership of Mitsubishi Motors, Mitsubishi Corporation, and local partner PT Krama Yudha. The three companies jointly announced the construction of a plant for the joint venture in the GIIC Industrial Park, 37 km east of Jakarta on the day of its establishment, held a groundbreaking ceremony for the new plant on March 24, and opened the plant on April 25, 2017. With an investment of 65 billion yen, the plant has 3,000 employees and is equipped with state-of-the-art facilities and functions with a maximum production capacity of 160,000 units per year.
The plant exports some of the produced vehicles to ASEAN countries, playing an important role as the second largest production base in the ASEAN region, following a plant in Thailand.
Mitsubishi models produced at the plant: Expander, Pajero Sport, Colt L300
Prev
Next
Installed 1,162 chargers for electric vehicles at each business site and facility.
Installed 1,162 chargers for electric vehicles at each business site and facility.
With the aim of improving the convenience of our employees who commute by electric vehicles (EVs) and plug-in hybrid vehicles (PHEVs), we have installed a total of more than 1,200 electric vehicle chargers at all of our business sites, including 1,162 additional chargers (8 rapid chargers and 1,154 standard chargers) in employee parking lots, company residences, and dormitories at our business sites in the Head Office (Minato Ward, Tokyo), Okazaki (Okazaki City, Aichi Prefecture), Kyoto (Kyoto City, Kyoto Prefecture), Shiga (Konan City, Shiga Prefecture), and Mizushima (Kurashiki City, Okayama Prefecture).
Chargers, including quick chargers, are installed in visitor parking lots as well, with regular chargers available for use for free.
Prev
Next
Commence operation of “Mitsubishi Motors Electric Vehicle Support”
Commence operation of “Mitsubishi Motors Electric Vehicle Support”
Mitsubishi Motors launched the “Mitsubishi Motors Electric Vehicle Support” program for owners of models in i-MiEV series and Outlander PHEVs—a package of support services that will enrich their EV experience, including a charging card that allows the owners to use the charging services at reasonable rates, which are provided through the network of Nippon Charging Service LLC (NCS).
The NCS charging services are available at Mitsubishi Motors dealerships, expressway service areas, parking areas, convenience stores, roadside stations, lodging facilities, and other service areas at reasonable rates.
Customers can choose from 3 plans according to their car lifestyles. The Basic Plan for 500 yen/month (excluding tax) is recommended for those who mostly charge at home, the Premium Plan for 1,500 yen/month (excluding tax) for those who often charge outside the home, and the Corporate Plan for 1,000 yen/month (excluding tax) for corporate customers.
In addition, the program comes with a full range of support services, including a members-only smartphone app that helps the driver find available chargers, towing arrangements in the event of an accident or power failure, and a comprehensive road service that includes compensation for home returning and accommodation expenses.
Prev
Next
MMTh opened the first ever test course outside Japan.
2016
Misconduct revealed in fuel consumption tests
Misconduct revealed in fuel consumption tests
In 2015 (2015), NMKV Co., Ltd. (established as a joint venture between MMC and Nissan Motor Co., Ltd.) measured the fuel economy of an ek wagon developed by ther Company as a reference for the development of new models. When it was found that there was a large discrepancy between the measured fuel economy and the fuel economy reported to the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism, the Company investigated the cause.
Upon receiving an NMKV’s report on the discrepancy, Mitsubishi Motors investigated the cause and found that the type of approval test results reported to the ministry had been rigged to make the fuel efficiency data look better. In response, the Company reported the misconduct in the fuel efficiency test to the ministry and held a press conference.
A series of investigations uncovered fraudulent activities involving 20 models that were sold in the past as well as vehicles currently on market, and this led to the resignation of the then president.
Furthermore, a Special Investigation Committee consisting only of independent outside experts was established to conduct an objective and thorough investigation. The investigation report was received on August 1 and further reported to the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism.
[Overview of the investigation report]
1. The running resistance in the fuel consumption test was measured by the "high-speed coasting method" instead of the "coasting method" prescribed by domestic laws and regulations.
2. Preferable data was arbitrarily selected from the data set obtained by conducting a high-speed coasting test method.
3. Driving resistance was determined by desk calculation using data from other vehicles.
A coasting test was designated in 1991 under Japanese law. At that time, however, Mitsubishi Motors was reportedly striving to expand its domestic sales, and under the pressure to sell as many vehicles as possible, it kept using the high-speed costing test, which requires less testing time, thus systematically conducting fraudulence to reduce required procedures.
After this misconduct came to light, the Company stopped making mini vehicles until July of the same year, while at the same time correcting its fuel efficiency data and paying damage compensations to its customers.
Following a series of quality problems identified in 2000, 2004, and 2012, efforts to prevent the recurrence of such problems were made by ensuring compliance and adhering to the spirit of “Customer First” and “Safety First.” But again, the Company committed another transgression betraying the trust of its customers.
Prev
Next
Set up Special Investigation Committee in connection with the acquisition issues of certification of conformity.
Changed the name of Nagoya Plant to Okazaki Plant.
Launched Electric DRIVE STATION
Launched Electric DRIVE STATION
The Dendo Drive Station, equipped with a solar power system and V2H equipment, *1 is an outlet capable of charging electric vehicles (EVs) with solar power as well as supplying electricity back to the outlet. At the store, the role of electric vehicles in Japan's energy problems and the value of electric vehicles' external power supply function in times of disaster are introduced with digital signage systems *2 and tablet terminals. In the Lifestyle Corner, which resembles a dining room of an ordinary household, there are demonstrations of power outages that demonstrate power supply by V2H devices in the event of a power outage, and demonstrations of 1,500 W experience that enable multiple household appliances to be used simultaneously with an electric vehicle's 100 V AC power supply (1,500 W).
Mitsubishi Motor has been promoting the nationwide rollout of the next-generation “Electric Drive Station,” and as the first such store, the Setagaya Store (Setagaya-ku, Tokyo) of Kanto Mitsubishi Motors Sales Co., Ltd. (currently East Japan Mitsubishi Motors Sales Co. Ltd.) was reopened after renovation.
Please refer to the following website to check the current installation status of Electric DRIVE STATION. (in Japanese only).
> https://www.mitsubishi-motors.co.jp/carlife/phev/dendo/index.html
Notes:1. V2H, which stands for vehicle-to-home, allows an EV to transfer the stored electricity to your home.
2. Digital signage system is a platform that distributes content to digital screens within its network.
Prev
Next
Nissan Motor Co., Ltd. acquires 34% of the Mitsubishi Motors
Nissan Motor Co., Ltd. acquires 34% of the Mitsubishi Motors
On May 12 of the same year, Nissan Motor Co., Ltd. (Nissan Motor Co., Ltd.) signed a basic agreement for a capital and business alliance to acquire 34% of the total number of shares issued by the Company through third-party allotment.
Based on the agreement, the parties entered into a strategic alliance agreement on May 25.
As all the requirements in the payment concerning the third-party allotment were met following due diligence by Nissan, Nissan acquired 34% of Mitsubishi Motors’ outstanding shares for approximately 237.3 billion yen, making Nissan the largest shareholder of the Company as well as bringing the Company under the umbrella of the Renault-Nissan Alliance.
On September 15, 2017, the Renault-Nissan-Mitsubishi Alliance announced ALLIANCE 2022, a plan to double synergies to 10 billion euros per year in the six years to 2022, in a bid to accelerate collaboration in shared platforms, powertrains, next-generation electric vehicles, automated driving, and connected technologies.
Prev
Next
2017
Receipt of an Order to Take Measures in accordance with the Premiums and Representations Act and an order to pay a surcharge
Receipt of an Order to Take Measures in accordance with the Premiums and Representations Act and an order to pay a surcharge
With regard to the misconduct in fuel economy tests discovered on April 20, 2016 (2016), our company received an order of action and a surcharge payment order from the Consumer Affairs Agency based on the Premiums and Representations Act (hereinafter referred to as the "Premiums and Representations Act") on the grounds that the fuel economy values displayed in the catalogs and advertisements of Sony products were shown to general consumers to be significantly better than the actual values, and that this was a misrepresentation of good quality as defined in the Act against Unjustifiable Premiums and Misleading Representations.
The Agency ordered us to immediately report to the Commissioner of the Consumer Affairs Agency in writing that the Company would take steps to prevent a recurrence and would not commit similar violations in the future. Additionally, the Company was ordered to pay a penalty of 485.07 million yen based on the penalty system introduced and made effective on April 1, 2016, and paid the penalty on March 31, 2017.
This is to be the first time that the Consumer Affairs Agency has issued a surcharge payment order since the enforcement of the revised law.
Prev
Next
Introducing the Matching Gift Program for in-house donations
Introducing the Matching Gift Program for in-house donations
Mitsubishi Motors introduced the Matching Gift system, where the company donates an amount equal to the amount reserved for the Mitsubishi Motors STEP Fund * to support the activities of the fund.
Accordingly, the Company’s donation began in FY2017.
On February 17, 2019, a major donation project utilizing this program involved the construction of an elementary school building in the Philippines. The total amount of donations at this time was 3 million yen, including employee donations and the same amount donated by the company.
Note: The Mitsubishi Motors STEP Funds is a voluntary fund-raising campaign established in FY2009 and operated by employees of the Company and its Group companies. Participants donate 100 yen per month (200 yen in case of lump-sum payment) to the fund.
Over the ten years through the end of 2018, a total of more than 4,000 people had participated with a total of approximately 34.78 million yen collected.
Prev
Next
Opened a day-care center for employees at Okazaki Plant.
Established MMKSI in Indonesia.
Renovated Mitsubishi Motors Pavilion at KidZania Tokyo
Announced Alliance 2022.
Released mid-term business plan “DRIVE FOR GROWTH”.
Started conducting tests in Europe to verify power grid stabilization (V2G).
Established the brand message: Drive your Ambition.
Kyoto Plant - Shiga Achieves Cumulative Engine Production of 10 Million Units
2018
Established MMFS in the Netherlands.
Opening a “Training Room to Learn from Mistakes” at Okazaki Plant
Opening a “Training Room to Learn from Mistakes” at Okazaki Plant
The Company opened a “Training Room to Learn from Mistakes” on the first floor of the Main Technical Building in its Okazaki Plant as part of measures to prevent misconduct such as a case of data falsification which was brought to light on April 20, 2016. The training room is intended to provide its employees opportunities to reflect on the scandals (mistakes) the Company has made over the quality and safety of vehicles as well as to explore measures to prevent the recurrence of such misconduct.
Training sessions were held immediately after the training room was opened. By May 2019, all employees of the plant, from executives in the Development Department to general employees, had completed the training sessions.
Mitsubishi Motor continuously strives to ensure that the lessons of the past are not forgotten to prevent scandals from happening again.
Prev
Next
Violation of the Act on Regulation of Technical Training revealed
Violation of the Act on Regulation of Technical Training revealed
Under the Foreign Technical Intern Training Program, trainees from the Philippines worked at the Company’s Okazaki Plant to acquire welding and painting skills. However, an on-site investigation by the Ministry of Justice and the Foreign Technical Internship Organization revealed that the trainees had been instructed to engage in vehicle assembly, which was not covered by their training plan.
Moreover, it was found out that similar inappropriate instructions had been given to trainees over the ten years from 2008.
Following the investigation results, on January 25, 2019, the Company received 27 notices of cancellation of the technical training plan and one improvement order from the Ministry of Justice and the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare in accordance with the Act on Proper Technical Intern Training and Protection of Technical Intern Trainees, which went into effect in November 2017.
Prev
Next
MMTh achieved production of a cumulative total of 5 million units.
Commence Demonstration Experiment of Power System Stabilization (V2G) in Japan
Commence Demonstration Experiment of Power System Stabilization (V2G) in Japan
Mitsubishi Motors, Kyushu Electric Power Co., Inc., the Central Research Institute of Electric Power Industry, Nissan Motor Co., Ltd., and Mitsubishi Electric Corporation jointly announced that, starting June 2018, they will start verifying the technology of V2G (Vehicle to Grid), which supplies electricity from electric vehicles (hereinafter “EVs”) to the power grid, with an aim to use EVs as a tool to balance the supply and demand of electricity.
This implementation test is designed to verify the possibility of using the electric power stored in EVs to adjust power supply and demand by discharging the electric power to the electric power system.
As V2G is expected to serve as a new technology to buffer the variability of renewable energy such as solar power, which is growing rapidly, they were performed as an initiative toward realizing a low-carbon society.
Part of the tests was subsidized by the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry's Agency for Natural Resources and Energy (executive body: Sustainable Open Innovation Initiative) under its “Building Virtual Power Plant Using Customer-Side Energy Resources” program.
Prev
Next
Started adopting the new store design at distributors worldwide.
The Then Chairperson of the Board of Directors Arrested on Suspicion of Violating the Companies Act
The Then Chairperson of the Board of Directors Arrested on Suspicion of Violating the Companies Act
The then-chairperson of the board of directors of Mitsubishi Motors was arrested by the Special Investigation Department of the Tokyo District Public Prosecutors Office on suspected violation of the Financial Instruments and Exchange Act, namely making false disclosures in annual securities reports of Nissan Motors Co., Ltd. (hereinafter “Nissan”).
Following the arrest of the suspect, a resolution to discharge him as representative director and chairperson was adopted at the board meeting of November 26, on the grounds that it had become difficult for him to continue duties as representative director and chairperson. The Company released an announcement on January 28, 2019 that, according to an internal investigation by an outside law firm to identify similar cases of misconduct within Mitsubishi Motors, the suspect had received improper payments as Managing Director from Nissan-Mitsubishi BV (hereinafter “NMBV), a 50-50 Netherlands-based joint venture established in June 2017.
No cases of misconduct were found at any of the Company’s affiliates other than NMBV and Mitsubishi Motors.
The then-chairperson was discharged from the position of director, following approval at the 50th Ordinary General Meeting of Shareholders held on June 21, 2019.
Prev
Next
2019
Moved the headquarters to Shibaura, Minato City.
Announced the results of the internal investigation regarding the misconduct of the former chairman of the board of directors.
Opened a day-care center for employees at the headquarters.
Transition to Company with three Committees
Transition to Company with three Committees
Mitsubishi Motors announced in December 2015 that it would transition to a "Company with Corporate Auditors." However, the transition was postponed due to the discovery of a fuel efficiency scandal.
Based on the recognition that it was necessary to further enhance corporate governance, on May 9 of the same year, Mitsubishi Motors announced a plan to transition from a company with an audit & supervisory board to a company with three committees in order to achieve swift business execution in response to environmental changes by clearly separating supervisory and execution function and ensuring the soundness and transparency of management through strengthening of supervision and risk management. The resolution, which was placed on the agenda at the 50th Ordinary General Meeting as a partial amendment to the Articles of Incorporation, was approved at the same meeting. Consequently, the Company transitioned to a company with three committees effective the same day.
Prev
Next
2020
Concluded a disaster cooperation agreement with Minato City for the first time in Tokyo.
Policy for Mitsubishi Motors Social Contribution STEP Activities Revised, New Communication Words and Logo Marks also Set
50 Years of Foundation
Renault, Nissan and MMC Announce New Alliance Initiatives to Enhance Competitiveness and Profitability
Releases Medium-term Business Plan "Small but Beautiful"
Formulated New Environmental Plan Package
Mitsubishi Motors Launches First Overseas Production of Outlander PHEV in Thailand
2021
MMC Diamond Finance Co., Ltd. Renamed Mitsubishi Motors Finance Co., Ltd.
Launch of Large-Scale Rooftop Solar Power at Production Plant in Thailand
Renovated Mitsubishi Motors Pavilion at KidZania KOSHIEN
Production Ended at PMC and Factories Shut Down
Initiation of Demonstration Tests to Promote Carbon Neutralization
The World Premiere of the AirTrek Electric Vehicle at the Guangzhou Motor Show in China
2022
Renault-Nissan-Mitsubishi Unveils Alliance Roadmap
Renault-Nissan-Mitsubishi Unveils Alliance Roadmap
A press conference titled “Alliance 2030: Best of 3 Worlds for New Future” by the Alliance of Renault, Nissan, and Mitsubishi Motors was broadcast live, connecting the Tokyo and Paris venues.
At the press conference, the Alliance defined a common 2030 roadmap on pure-EV and Intelligent & Connected mobility, sharing investments, and made an announcement of its plan to make an additional investment of a total of 23 billion euros in the following five years on electrification, leading to 35 new EV models by 2030 as well as its vision to bring a highly competitive and attractive offer to all customers through a common Alliance battery strategy, breakthrough battery innovations, and a planned 220 GWh production capacity.
The Alliance also unveiled its plan to reinforce its presence in Europe with two new models, including the New ASX based on Renault best-sellers.
Prev
Next
New Paint Factory Completed and Opened in Thailand
Signed Positive Impact Finance Agreement with MUFG Bank, Ltd.
Signed Positive Impact Finance Agreement with MUFG Bank, Ltd.
Positive impact finance, a type of financing for corporates with unspecified use of funds, comprehensively analyzes and evaluates the impact (positive and negative) of corporate activities on the environment, society and the economy with an aim to provide continuous support for such activities, based on the Principles for Positive Impact Finance and implementation guidelines formulated by the United Nations Environment Programme Finance Initiative (UNEP FI).
In selecting the themes for this agreement, the Company chose activities that contribute to achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and align with its material issues.
Mitsubishi Motor’s major activities recognized as having an impact on achieving the SDGs
- Contributing to a decarbonized society through electrified vehicles
- Reducing environmental impact
- Enhancing the safety and security for drivers
- Contributing to the economies and societies of the ASEAN region
- Promoting diversity
Prev
Next
Transition from First Section of the Tokyo Stock Exchange to Prime Market
Concluded Disaster Cooperation Agreements with 200 Local Governments
Concluded Disaster Cooperation Agreements with 200 Local Governments
Since 2019, Mitsubishi Motors has been making full-scale efforts to conclude disaster cooperation agreements with local governments across Japan. The number of agreements reached 200 in July 2022.
The Company and its affiliated companies are driving forward the DENDO Community Support Program to promote the conclusion of disaster cooperation agreements with local governments so that, in the event of a power outage due to a disaster, the Company can save the time to confirm required information with them and quickly provide its EVs—Outlander and Eclipse Cross plug-in hybrid electric vehicle (PHEV) models —to disaster-stricken areas, evacuation sites, and other relief centers upon request.
In 2023, the Company achieved the goal of entering into disaster cooperation agreements with local governments throughout Japan with the total exceeding 250. Going forward, the Company will strive to promote the understanding and widespread use of EVs/PHEVs, as well as to strengthen support systems for disasters.
Prev
Next
Exhibited at Kidzania Fukuoka
Achieves Cumulative Export of 5 Million Units from Thailand
2023
Renault-Nissan-Mitsubishi Alliance Unveils New Initiatives Aimed at Raising the Bar Higher
Releases Medium-term Business Plan “Challenge 2025”
Launches Forest Conservation Activities at “Okazaki Outlander Forest”
Establishes an Off-Road Test Course in the Tokachi Research Institute
Renames MMC Wing Inc. to Mitsubishi Motors Wing Co.
Kyoto Plant Achieves Cumulative Engine Production of 40 Million Units